What Does It Really Mean When Your Triiodothyronine (T3) Levels Are Low?
According to a 2010 study published in the journal StatPearls, your thyroid gland is vital in metabolism, growth, and maintaining essential body function by releasing certain hormones into the bloodstream. Triiodothyronine (T3) is one of two major hormones secreted by your thyroid gland (via Healthline). Triiodothyronine is a crucial endocrine hormone connected with nearly all human cells and supports their sustenance, as stated in a 2021 study published in the journal Frontiers in Endocrinology.
The T3 test is one way to measure your T3 levels. According to Cleveland Clinic, a T3 test is a special blood test used to diagnose thyroid conditions. It comes in two forms. The first is the total T3 test, which measures free and bound triiodothyronine levels. The second is the free T3 test, which measures only free triiodothyronine levels. For T3 to be normal, total T3 needs to be within 75–195 ng/dl and free T3 0.2–0.5 ng/dl (via the University of Rochester Medical Center). So, what does it really mean when your triiodothyronine (T3) levels are low?
Continue reading to understand more about low triiodothyronine levels and the available treatment options.
What low T3 levels indicate
Both total and free T3 tests can depict whether you have high or low T3 levels (via Medline Plus). If a blood test reveals low T3 levels, you might have hypothyroidism, also known as an underactive thyroid, according to WebMD. The source further notes that hypothyroidism has various causes, including medications, radiation therapy, recent thyroid surgery, iodine deficiency, and pregnancy. When the thyroid gland is underactive, the body can't produce enough thyroid hormones, which it needs to regulate metabolism. According to Mayo Clinic, hypothyroidism throttles many metabolic processes in the body, which can result in various thyroid disorder symptoms, such as fatigue, weight gain, muscle weakness, and constipation.
Healthline notes that a distinction is often made between primary, secondary, and tertiary hypothyroidism: According to the source, primary hypothyroidism is associated with chronic inflammation of the thyroid gland. Autoimmune conditions like Hashimoto's thyroiditis are usually linked to primary hypothyroidism. Healthline also notes that secondary hypothyroidism is usually caused by a problem in the pituitary gland. According to a 2011 study published in the Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, tertiary hypothyroidism involves a disorder of the hypothalamus — another brain region.
Treatment options for low T3 levels
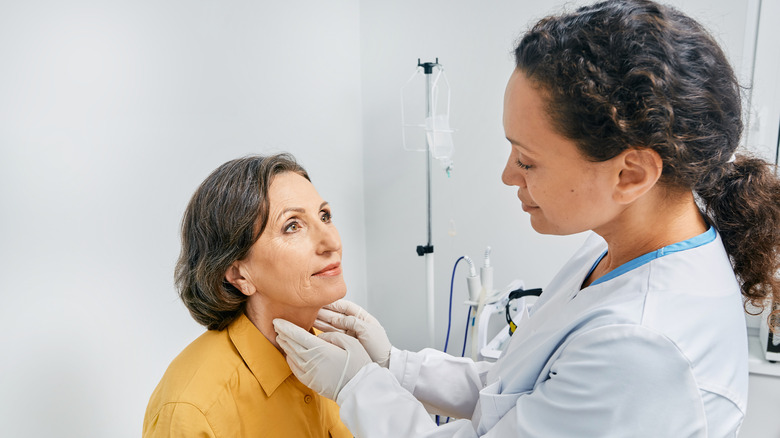
If you suspect an underactive thyroid, the first step is usually a detailed discussion with a doctor and taking your medical history. Your doctor might detect an enlargement of the thyroid gland or nodular changes by palpating the neck region, per Stanford Medicine. If you're asked to take a thyroid test that reveals low T3 levels, the missing thyroid hormone thyroxine needs to be replaced. According to the American Thyroid Association, thyroid hormones are essential for the health of cells in the body.
So, if the thyroid gland is underactive, the missing hormones must be supplied from outside by taking the thyroid hormone levothyroxine, per Medical News Today. The American Thyroid Association notes that this drug is similar to the body's own hormone called thyroxine. By taking the tablet every day, the lack of endogenous production can be replaced. Medical News Today, however, notes that the treatment doesn't cure the condition. The drug only allows thyroid hormone levels to return to normal.