Peg Tube Versus G Tube: What's The Difference?
Nutrition is essential for life, but some medical conditions can make eating and drinking difficult, which leaves us in need of feeding assistance. This is when the surgical procedure known as gastrostomy comes in. According to the Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe (CIRSE), a gastrostomy is vital for people who can't swallow normally due to neurological reasons, like stroke, or other conditions that cause anatomical issues and gullet obstruction. The University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC) further notes that gastrostomy can be performed using a percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) or an open surgical procedure. Patients are normally under local anesthesia during the procedure, per UPMC.
According to a 2012 study published in the American Journal of Alzheimer's Disease & Other Dementias, medical trends indicate that PEG tube placements increased by 38% between 1993 and 2003 among elderly patients. As gastrostomy becomes more popular in the medical world, it's crucial to gain deeper insight into the PEG tube and G-tube procedures in order to understand how they differ.
What's the difference between PEG tubes and G-tubes?
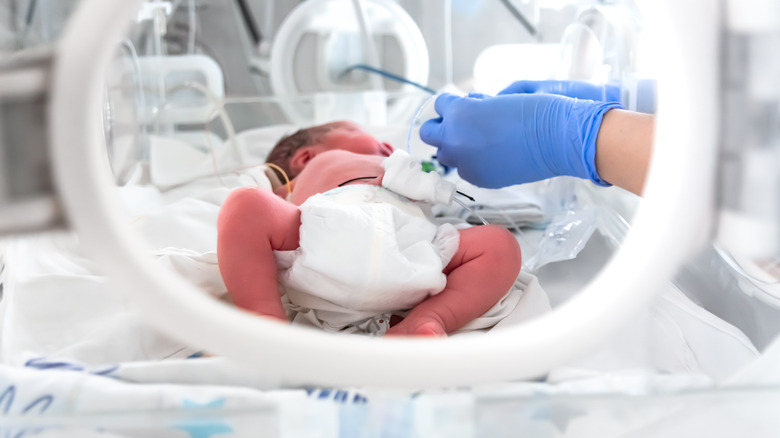
During a gastrostomy, a surgeon places a small feeding tube into the stomach to transport food, per the National Health Service (NHS). According to MedlinePlus, the G-tube (or gastrostomy tube) is the name of the surgical device that's usually placed in the stomach. The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia notes that G-tubes can be placed using a standard open surgery in the operating room. According to The Nemours Foundation, during an open surgery, the surgeon makes an incision on one side of the abdomen and into the stomach. The surgeon then places the G-tube through the incision before stitching the stomach around the tube. To keep the tube in place, the surgeon stitches the stomach to the abdomen wall. According to the UPMC, this procedure requires general anesthesia.
The PEG is another surgical method that's less invasive but also involves a small incision on the stomach, according to UPMC. The PEG procedure usually starts with the surgeon guiding a gastroscope through the mouth and into the stomach. A gastroscope is a type of endoscope with a camera attached to the end that provides a clear view of the stomach's insides. From the internal examination, the doctor will then decide where to make an incision in the stomach for the tube to be inserted, per UPMC. The main difference between a standard G-tube and PEG tube is that one is less invasive, whilst the other is full open surgery.
Pros and cons of gastronomy surgery
According to a 2014 study published in the journal Paediatrics and Child Health, children — especially those with neurological impairment — experience various nutritional benefits after gastrostomy placement. It helps reduced feeding time, chest infections, vomiting, and choking episodes, making life easier for patients and their caregivers. Another advantage of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy is that the tube can be removed when a patient regains the capability to eat and drink (via the NHS).
Generally speaking, possible complications of using a feeding tube can be compared to starting a new diet regimen. The patient might experience common complications like constipation and dehydration, per Stanford Medicine. A 2011 study published in the journal Proceedings of the Nutrition Society revealed other various complications, including peritonitis, hemorrhage, pneumonia, and esophageal lacerations.
A 2003 study published in the journal Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care also notes that people receiving nutrition via PEG or G-tubes may experience a high incidence of gram-negative pneumonia.