What Does It Really Mean When Your Thyroxine (T4) Levels Are Low?
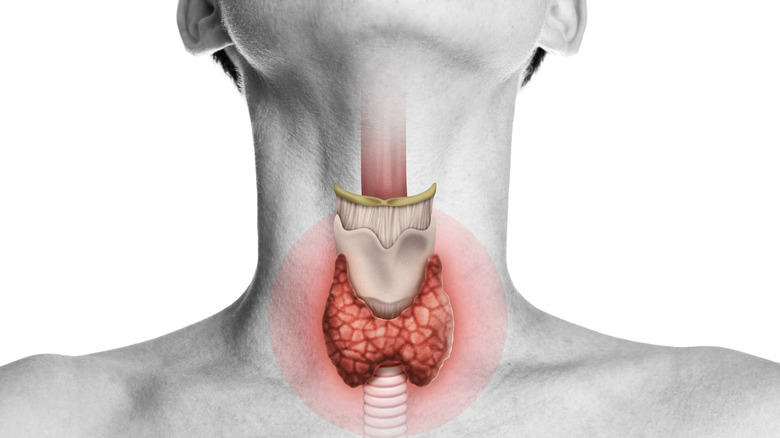
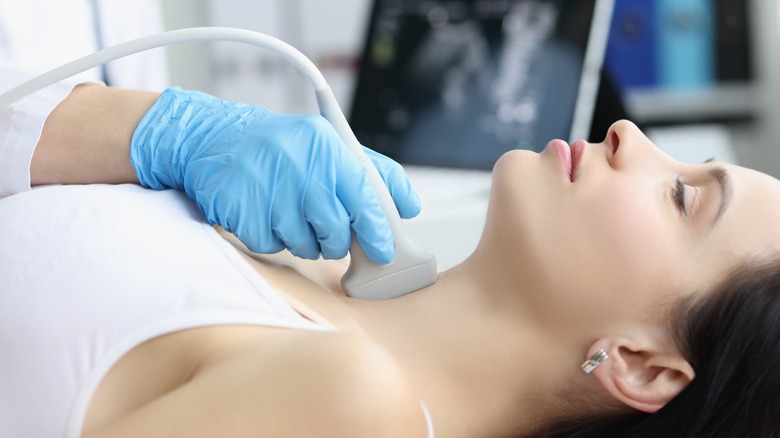
According to the National Cancer Institute, thyroxine — also called T4 — is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland. This hormone increases the rate of chemical reactions in the body. The importance of T4 can't be over-emphasized, especially concerning optimal growth and development, per the National Cancer Institute — having low thyroxine levels can be problematic. According to the National Health Service (NHS), having a blood test to check your hormone levels is the most accurate way to determine if there's an issue with your thyroid function. This claim is reiterated by the American Thyroid Association, which lists various thyroxine tests, including free T4 (FT4) and free T4 index (FTI).
A normal T4 level should range between 5.0 and 11.0 micrograms per deciliter of blood (via Cleveland Clinic). If your T4 test result falls below this range, your thyroid and overall health may be at risk. Here is what you need to know about your thyroxine levels and the various treatment options for low thyroxine.
What low T4 levels indicate
WebMD says lower-than-normal T4 levels may indicate that you have hypothyroidism or underactive thyroid disease, a common disorder that makes it difficult for your thyroid to produce enough thyroxine. This thyroid hormone deficiency can be life-threatening without the correct treatment (via Cleveland Clinic).
Statistics from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases reveal that about 5 out of 100 people above 12 years old in the United States have hypothyroidism. The institute notes that pregnant women and people with a family history of thyroid disease are more susceptible to hypothyroidism. People with other underlying medical conditions may also be at risk of hypothyroidism. The National Human Genome Research Institute notes that 10% of women battling Turner Syndrome may develop hypothyroidism. As for the symptoms of low T4 levels, the NHS lists various ones, including weight gain, muscle aches, loss of sex drive, and tiredness.
Treatment options for low T4 levels
According to the Cleveland Clinic, a significant part of managing hypothyroidism symptoms with medications depends on consistency. You may have to take drugs for the rest of your life, as well as assess your thyroxine levels and your treatment's effectiveness over the years, per the Cleveland Clinic. According to the Mayo Clinic, the synthetic thyroid hormone known as levothyroxine is often used for treating hypothyroidism. This medication can restore thyroxine hormone and lower hypothyroidism-related cholesterol levels. The NHS also explains that levothyroxine enables various functions, including the health of your heart, bones, and muscles, and better digestion and brain development. However, some side effects or drug interactions might occur. Therefore, it is important to be forthcoming with your doctor as you continue your levothyroxine therapy.
Aside from medications, Healthline suggests going sugar-free. Sugar and processed foods can increase inflammation while limiting the conversion of thyroxine (T4) to triiodothyronine (T3). The source also recommends eating foods rich in vitamin B12 (like cheese, milk, and eggs) to help with fatigue and repair other damage caused by hypothyroidism. MedicalNewsToday warns against eating too many iodine-rich foods. These can trigger or worsen the condition in those who plan to diet to manage hypothyroidism symptoms.