Amoxicillin Explained: Usage, Dosage, And Side Effects
Amoxicillin is a common antibiotic prescribed to treat a variety of bacterial infections. Amoxicillin, also known as Amoxil, is part of the penicillin family of antibiotics and requires a prescription from your doctor for use (via StatPearls).
Because of its chemical structure, amoxicillin is classified as a beta-lactam antibiotic. Because beta-lactam antibiotics prevent the cell wall formation in certain bacteria, the bacteria cannot form a protective shell. As a result, antibiotics like Amoxil are more effective at killing bacteria allowing the body to recover from the infection quicker. According to the International Review of Neurobiology, amoxicillin is effective against a wide range of bacterial infections in both adults and children. This is one of the reasons amoxicillin is such a widely used antibiotic.
Before taking Amoxil, it is essential to note that it is an FDA-approved antibiotic that is generally safe when used as directed. Even though the drug is considered safe, it is necessary to understand why it is prescribed, its potential interactions, dosage, typical side effects, and more (via the FDA).
History of penicillin
Before antibiotics, a minor infection such as a mildly infected skin wound, throat infection, or ear infection could be fatal. As a result, the discovery of penicillin was crucial to human survival (via Science Museum).
According to the American Chemistry Society, penicillin was discovered by Alexander Fleming in England during the late 1920s. In the 1940s, during World War II, the need for this antibiotic rose. Because of the war, the United Kingdom could not produce enough of the medication. Thus, the United States stepped in to develop mass antibiotic production, which was a significant factor in ensuring supply during this time.
Furthermore, Animal Research reports that Beecham Research Lab experts discovered amoxicillin in 1972. This breakthrough revolutionized the treatment of bacterial infections, particularly respiratory-related infections of the lungs, throat, and ears. Amoxicillin's discovery was significant because it was thought to kill bacteria faster than the original penicillin formula due to its ability to be more lipid soluble.
Amoxicillin dosage
Amoxicillin is only available with a prescription from your doctor, and should be taken exactly as directed. The dose will differ between people depending on their underlying health conditions and the type of infection being treated (via the Mayo Clinic).
Medical News Today notes that Amoxil could be prescribed as a liquid, a chewable tablet, or in pill form. For those weighing more than 88 pounds, the average daily dose ranges from 750 to 2000 milligrams, divided into two to three doses. However, your doctor may prescribe a different amount based on your specific needs, which you must follow strictly. Suppose you stop taking the medication before finishing the entire course of treatment. In that case, your infection may worsen, or you could develop antibiotic resistance, rendering it useless if you develop another infection.
In addition, Amoxil is frequently prescribed to pediatric patients for bacterial infections. The patient's weight determines pediatric dosage. The average dose for pediatric patients is 20 to 40 milligrams per kilogram of body weight per day, divided into two to three doses (per the Mayo Clinic).
What you should discuss with your doctor before taking amoxicillin
When beginning a new medication, discussing medical history, allergies, and any other medications or over-the-counter supplements you may be taking with your doctor is critical. Some medicines can interact with others, potentially causing severe reactions or impairing medication absorption in your body. As a result, you may not receive the proper amount of medication needed to function correctly.
According to Drugs.com, you should not take amoxicillin if you are allergic to any antibiotic in the penicillin category. In addition, it is essential to let your doctor know if you are allergic or have had adverse reactions to cephalosporins.
A relevant health history, such as a history of asthma, kidney disease, seasonal allergies, phenylketonuria (PKU), or hives, should also be mentioned to your provider. Specific medical histories, such as PKU, will allow your doctor to exercise caution when prescribing certain forms of Amoxil that may contain additives that could harm your health (per MedlinePlus). Making a list of any previous medical history and medications can help your healthcare provider make the best and safest decisions for your care.
Advantages and disadvantages of amoxicillin
More than 15,922,907 amoxicillin prescriptions were written in the United States in 2020 (via ClinCalc). This statistic confirms that amoxicillin is a frequently prescribed medication. According to Wisegeek, one of the benefits of using amoxicillin and why it is commonly prescribed is the wide range of infections it can treat. Equally important, this antibiotic is reasonably priced, making it accessible to most people, regardless of insurance coverage. Furthermore, the medication is available in various oral forms, including several flavored liquid forms that improve the taste. Additionally, the side effects are less severe than with other antibiotics, and you can take this medication with or without food because it does not cause stomach upset.
Even though amoxicillin has many advantages, there are some disadvantages to using the antibiotic. Drugs.com reports that amoxicillin can reduce the efficacy of birth control pills. You should have another method of birth control, such as condoms, abstinence, or other options that your healthcare provider can help you decide on. It's also worth noting how frequently amoxicillin should be taken to be effective. In most instances, it must be taken three times a day, which can be difficult for some people.
Amoxicillin use in children
Similar precautions should be taken with children as with adults before giving amoxicillin. Your child's pediatrician should be aware of their medical history and any medications they are taking.
According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, most childhood illnesses are caused by viruses. Antibiotics would not be prescribed in this case. Amoxicillin, like other antibiotics, is only used to treat bacterial infections. As a result, requesting antibiotics as a precaution may lead to antibiotic resistance, especially in children. Healthline mentions that the most common side effects of amoxicillin in children are diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. If your child is taking amoxicillin for the first time, you should keep a close eye on them for any serious side effects, such as hives, swelling of the mouth or tongue, or difficulty breathing. In this case, you would dial 911 for emergency assistance. Furthermore, if your child has kidney disease or has had an allergic reaction to any penicillin-type antibiotic, you should consult your child's healthcare provider before using it.
Amoxicillin and Lyme disease
Lyme disease is caused by a type of tick known as a deer tick. Most infections occur when a tick remains attached to the body for more than a few days, according to WebMD. If left untreated, the bite causes bacteria to circulate throughout the body, affecting multiple areas of the body. The good news is that because bacteria cause it, antibiotics, specifically amoxicillin, can be used to treat it. To expedite healing, detecting the disease as early as possible is critical. However, the symptoms can be confused with other cold and flu-like symptoms, making it difficult to diagnose if you do not know you have been exposed to the tick.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that early diagnosis and treatment can prevent post-Lyme disease complications and shorten antibiotic treatment. Early symptoms may include a rash with a target or bullseye appearance. If this is the first symptom, adults and children should take amoxicillin three times daily for at least two weeks. If the disease has progressed to the heart muscle, intravenous medication and an extended dose of oral antibiotics, including amoxicillin, may be required for up to 21 days. In addition, if Lyme disease affects your joints, you may need amoxicillin for at least a month in addition to other antibiotics. Finally, the CDC warns that neurologic involvement is possible if the disease is not detected early. Hospitalization and various intravenous antibiotics may be required in this case.
What you should know about amoxicillin and mononucleosis
Mononucleosis (mono) is a contagious infection caused by the Epstein-Barr Virus. It is common among adolescents and young adults (via CDC). Because mono is a viral infection, antibiotics are rarely required. However, the symptoms of mono can be similar to those of strep throat, and secondary bacterial infection may be present in addition to mono. In this case, it is critical to understand the effects of antibiotics, specifically amoxicillin, on patients infected with the mono virus.
According to the Mayo Clinic, amoxicillin and other penicillin antibiotics should not be given to patients with mono because they can cause a rash. The rash does not indicate an allergic reaction to amoxicillin, but it may suggest that mono is the cause of your symptoms and warrants further investigation. The rash may spread all over the body. Your skin may itch, and its appearance may be alarming. The rash, however, will go away once the antibiotics are stopped. If you need to continue the antibiotic for secondary infection, your doctor may prescribe an antihistamine or other topical medications (via Healthline).
What happens if you take more amoxicillin than prescribed?
When taking any medication, it is possible to misread a label or forget that you have already taken a dose, resulting in an accidental overdose. An overdose, according to MedlinePlus, can range from mild to severe depending on how much medication was taken in excess. StatPearls reports that unintentional overdoses can occur when a patient's health conditions, such as geriatric patients or patients with renal insufficiency, are not considered. If there is a concern about renal function in these patient populations, a lower dose may be considered.
Furthermore, it is critical to keep the medication out of the reach of children. Some children have been known to gulp liquid medicines on their own because, believe it or not, when sweetened with a flavor they enjoy, it may taste good to them. The good news is that it is doubtful to result in a severe complication for an otherwise healthy child. It is critical, however, to contact Poison Control if you have any concerns about any medication your child may have obtained. Finally, it goes without saying that if your child reacts to the extra dose, has difficulty breathing, or appears distressed, you should call 911 (via Poison Control).
Antibiotic resistance can be caused by overuse of antibiotics
The World Health Organization (WHO) reports increased antibiotic resistance due to antibiotic misuse when a bacterial infection is not present and a virus causes symptoms or illness. There is also a concern in countries where antibiotics can be purchased without a prescription, contributing to antibiotic overuse. This makes it more difficult to treat certain bacterial lung conditions, sexually transmitted diseases, and infections that can occur in the bowel, such as salmonella.
According to the CDC, antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria that cause illness no longer respond to antibiotics that once killed them. As a result, the bacteria multiply, and the condition persists or worsens. The CDC also estimates that approximately 47 million antibiotic prescriptions are written unnecessarily, further antagonizing the problem with resistance. Resistant bacteria are difficult to treat and frequently necessitate hospitalization for IV antibiotics. The increased level of care required to treat the infection can lead to substantial medical bills, missed school or work, and additional trips to the doctor's office.
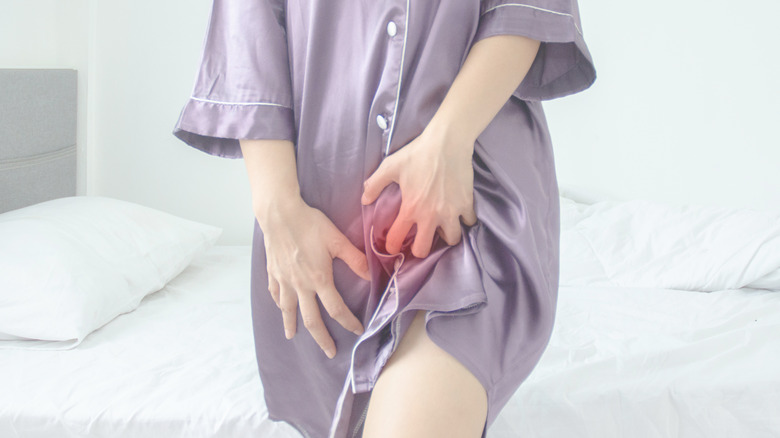
What you should know about amoxicillin and vaginal yeast infections
Antibiotics, including amoxicillin, can alter the body's balance of good and bad bacteria. According to Healthline, you may develop yeast infection when this happens. Yeast infections can appear in various parts of the body. Females taking antibiotics should be aware of the possibility of developing vaginal yeast infections. Vaginas naturally maintain a mildly acidic environment where yeast cannot grow. When you take antibiotics, the good bacteria that help keep the vagina acidic are destroyed along with the bacteria that cause illness. When this happens, the vagina can become a breeding ground for yeast, leading to a yeast infection.
Singlecare recommends avoiding prolonged wearing of wet bathing suits and tight clothing to help prevent yeast infections caused by antibiotics. Furthermore, douches, feminine hygiene products, and powders can alter the vaginal environment and should be avoided. Before taking antibiotics, consult your doctor to understand better the risks of developing a yeast infection.
Limiting your sugar intake and eating yogurt with live cultures or taking probiotics, according to Intermountain Healthcare, may help you avoid developing a yeast infection while on antibiotics.
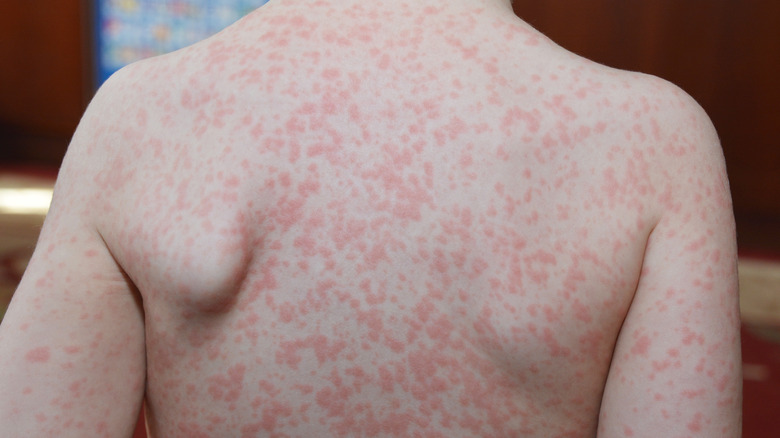
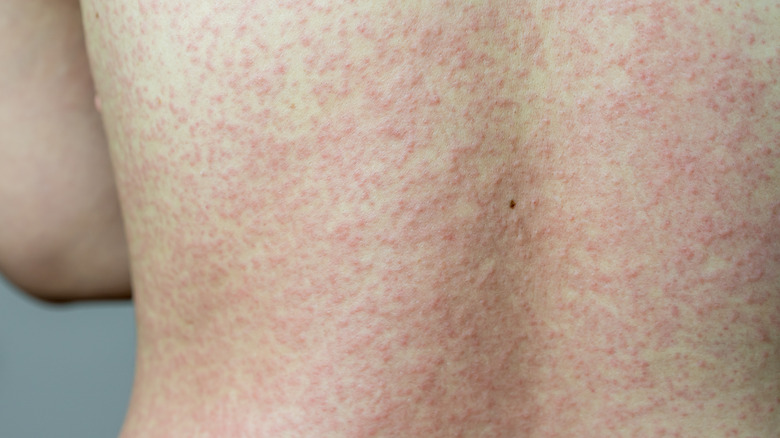
Getting a rash while taking amoxicillin does not always mean you have an allergy
If you or your child develops a skin rash after beginning amoxicillin treatment, this does not always indicate that you are allergic to the medication. Neha Seth, MD, a pediatrician, reported that 5% to 10% of children who take amoxicillin would develop a skin rash during treatment. She claims that the majority are non-allergy rashes.
According to Healthline, knowing how to tell the difference between a non-allergic rash and a true allergy is critical. A non-allergic rash usually appears three to ten days after beginning the antibiotic, but it can occur at any time during treatment. Small pale areas interspersed with red patches are described as the rash. This non-allergic rash is known as maculopapular.
On the other hand, an actual allergic reaction to amoxicillin can be life-threatening. Hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the face and lips are common symptoms of an allergic reaction. If this occurs, you should seek emergency medical attention. If a rash appears while taking the medication, consult your doctor before continuing (via Medical News Today).
Is amoxicillin safe to take during pregnancy?
Amoxicillin is a common antibiotic prescribed to pregnant women who develop bacterial urinary tract infections or respiratory infections during pregnancy (via Poison Control). The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classification for amoxicillin is a category B. This means multiple studies were performed on pregnant animals, resulting in no harm to the fetus. However, there are not enough human trials on pregnant women.
According to Healthline, amoxicillin is considered low risk and safe to take during any trimester of pregnancy. As with any antibiotic, you should complete the entire course while pregnant. Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are common side effects that you may experience while pregnant. If you have stomach upset, it is best to take the medication with food.
While taking medications during pregnancy can be frightening, amoxicillin and several other antibiotics are considered safe. Infections must be treated immediately, because they pose a much greater risk to the health of your developing baby. It is crucial to follow your doctor's instructions, as the impact of the bacteria can be far worse on your unborn baby than the antibiotics to treat it. Your doctor can guide you on the safest options (via Parents).
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea
A study published in the Journal of Pediatric Pharmacology and Therapeutics reports diarrhea as a common side effect when taking amoxicillin. However, it is more common when amoxicillin is combined with clavulanate. This combination antibiotic is known as Augmentin. Amoxicillin-caused diarrhea is usually mild and can be managed with over-the-counter anti-diarrheal medications and fluid replenishment. Antibiotics such as amoxicillin can, on the other hand, kill beneficial bacteria in your digestive tract. As a result of the disruption of normal flora growth in the gut while on antibiotics, certain types of serious infections may develop; however, they are rare.
Clostridium difficile (C-diff) is one antibiotic complication that can cause severe diarrhea due to the loss of beneficial bacteria in the bowel. C-diff is a bacterium, but it is not helpful to the gut. C-diff can only be cured with specific medication treatment. Even if you are not taking antibiotics, C-diff is highly contagious through contact with an infected person or surface. Hand washing with soap and water can help you avoid contracting this bug (via Yale Medicine).