What's The Difference Between Tennis Elbow And Elbow Bursitis?
You've had that pain in your elbow for a while, and it's only getting worse. Even if you don't play sports, it may be a condition called tennis elbow. But depending on where the pain is, it could be elbow bursitis.
The elbow is where the single upper bone of the arm meets the two bones of the forearm (via Arthritis Foundation). The joint there is a synovial hinge joint that, rather than rotate, like the hip, allows the elbow to bend and straighten (per Medical News Today). The joint is complex, as it connects the multiple bones of the arm with ligaments. You use your elbow every day, and it's usually overloading after so much use or simply use over time that causes elbow issues, such as inflammation.
According to Healthline, the bursa is a thin sac of fluid located on the tip of the elbow to help cushion it and allow the skin over it to move smoothly. The bone that creates the protruding tip on the end of the elbow is called the olecranon. The bursa can fill with excess fluid and become inflamed from use over time, sudden trauma, infections, or frequently putting pressure on the elbow (via Cleveland Clinic). When this happens, it is called elbow bursitis, and the elbow joint can be swollen, painful, and may be challenging to use. Elbow bursitis is diagnosed with a physical exam, but possible infections will require further testing, such as a blood test, x-ray, or ultrasound.
Tennis elbow affects tendons
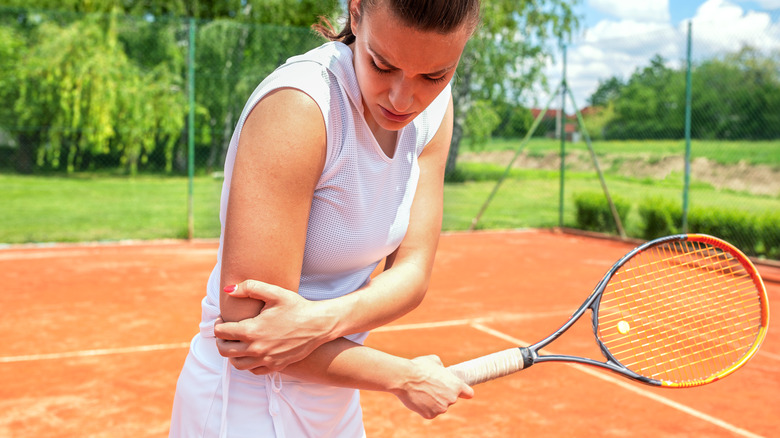
Although it's in the same area, tennis elbow or lateral epicondylitis is not the same as elbow bursitis, as per Cleveland Clinic. Tennis elbow involves the tendons in the elbow being overloaded by repetitive motion (per Mayo Clinic). Whereas bursitis affects the bursa at the tip (via Cleveland Clinic), tennis elbow occurs where the forearm tendons attach to the bony epicondyle on the outside of the elbow above the tip, explains Mayo Clinic. The pain can spread further down the forearm and even into the wrist as the forearm muscles contracting trigger it. Motions like painting, or swinging a tennis racket can lead to this repetitive overuse.
Despite their differences, treatments for the two conditions are similar. Treatments for elbow bursitis include heat, physical therapy, ice, corticosteroid injections, anti-inflammatory medications, immobilization, or surgery (per Cleveland Clinic). Infections that cause elbow bursitis are the main difference and will require antibiotics. Tennis elbow treatments include rest, ice, anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, adjusting movement techniques, injections, or surgery (via Mayo Clinic).
According to the National Health Service, tennis elbow is the most common cause of persistent elbow pain and affects 1% to 3% of the population annually. Since common repetitive movements cause it, tennis elbow can be hard to prevent. Likewise, elbow bursitis is fairly common, with most cases caused by physical trauma rather than infections, reports Cleveland Clinic. To help prevent it, try resting the joint between strenuous exercise or activity sessions, and wear elbow pads when necessary.