This Is What Happens To Your Body If You Don't Treat Lymphedema
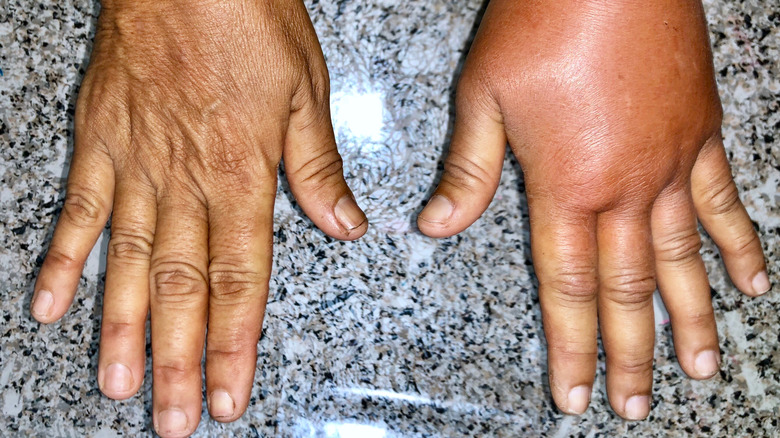
Lymphodema is an inflammation caused by a disorder in the lymphatic system, according to Cleveland Clinic. The condition usually affects the lymph nodes, which rid the body of germs and other waste products (via Medical News Today). The causes of lymphedema vary and include lack of activity, trauma, obesity, infection, tumors, and radiation therapy, per Cleveland Clinic. Johns Hopkins Medicine states that lymphedema may be a potential side effect of breast cancer treatment due to the surgical removal or radiation of lymph nodes which can in turn lead to the swelling that marks lymphedema. Cancer survivors may develop this condition immediately or years after successfully completing their treatment.
If you currently have lymphedema, you might notice some changes in your body that might be linked to the symptoms of lymphedema. It's important to discuss this with your doctor to understand the available treatment options. Here's what happens to your body if you don't treat lymphedema.
Symptoms of untreated lymphedema
According to Medical News Today, lymphedema is progressive and, if left untreated, can lead to more severe complications, including skin infections like cellulitis. Cellulitis infects the deeper layers of your skin as well as other underlying tissues, potentially leading to fatal consequences if proper treatment measures are not taken, per the National Health Service (NHS).
A 2009 study published in the journal Lymphatic Research and Biology states that lymphedema patients can experience several psycho-social problems caused by the condition. Due to the skin infections associated with the condition, some people become dissatisfied with their body image. Some people might even get depressed and experience a reduced quality of life.
According to WebMD, lymphedema symptoms can happen anywhere on the body, chest, head, and even genitals. They include tight or dry skin and heavy feelings in the limb. It's important to report these common symptoms to your doctor.
Prevention & treatment of lymphedema
According to the Mayo Clinic, lymphedema has no cure. Treatment primarily focuses on preventing complications and reducing any swelling. To properly manage the symptoms of lymphedema, it's recommended that you eat a healthy diet, engage in physical activity if possible, and do your best to keep the affected skin clean and moisturized.
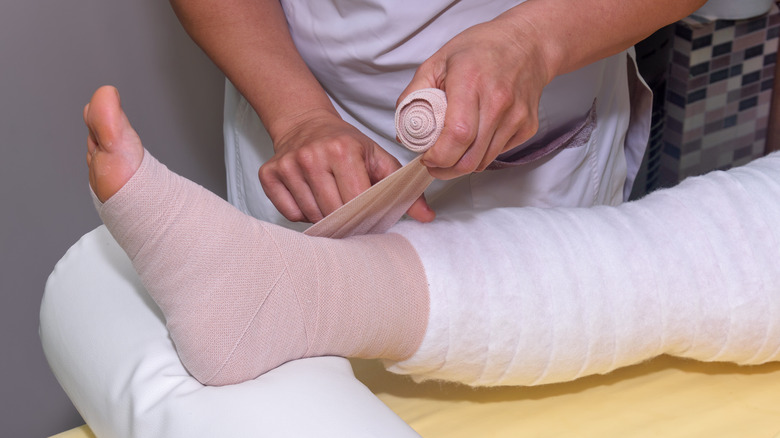
According to Cancer Research UK, activities like walking, swimming, and yoga might help drain lymphatic fluids. Your doctor might also combine multiple treatments (that include massages and the use of compression pumps) into a decongestive lymphatic therapy, per Mayo Clinic. Besides the therapy, some people with lymphedema rely on various medications, such as antibiotics, which help manage symptoms of cellulitis. When the condition becomes severe, surgical removal of fibrous tissues might be required.
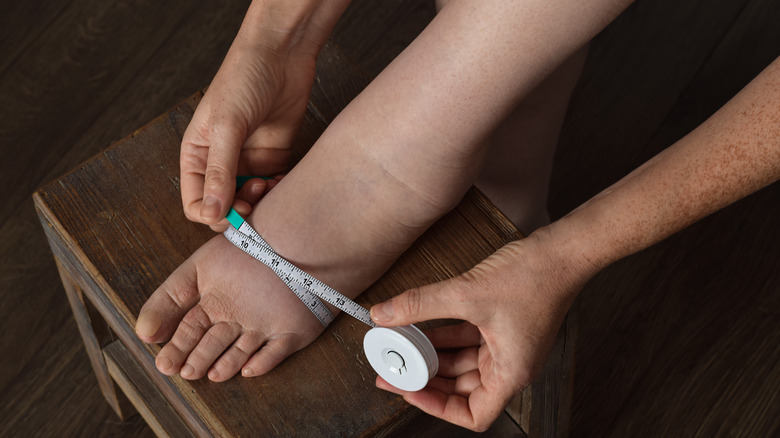
However, this won't happen without an effective diagnosis. A 2017 research review published in the journal Physical Therapy notes that doctors might first assess a patient's clinical history or physically examine their tissue quality. The source indicates that other tests, including symptomatology and measurement of limb volume, can further help determine if an individual has lymphedema.