Here's How To Treat Bed Bug Bites
"Don't let the bed bugs bite" is great advice, but it may be easier said than done. You may not even realize that bed bugs are real and do bite. Can you identify these troublesome bites, and do you know how to treat them?
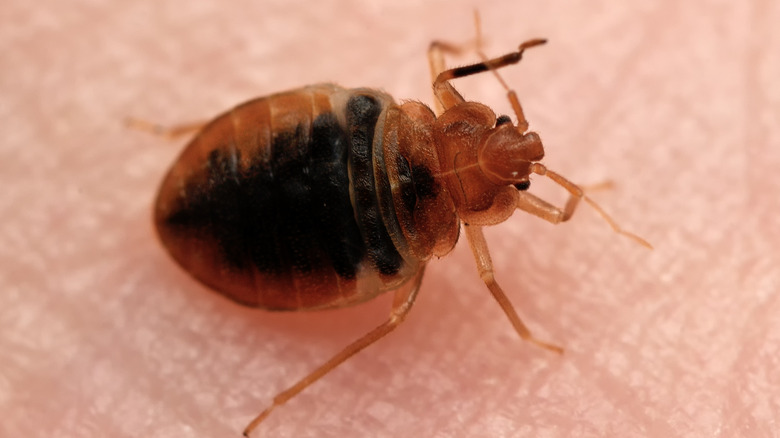
The oldest and, therefore largest bed bugs are the size of an apple seed, reports WebMD. They are brown insects that survive by eating the blood of animals, including humans. Bed bugs crawl reasonably quickly and are very good at hiding. They can slip into very tiny crevices and like to travel via hitchhiking on clothing, luggage, or used furniture. Once they are in your home, an infestation can occur if they are not handled quickly. It's not always easy to identify a bed bug problem, since they are so small, active at night, and leave marks that could be attributed to several other common pests or ailments.
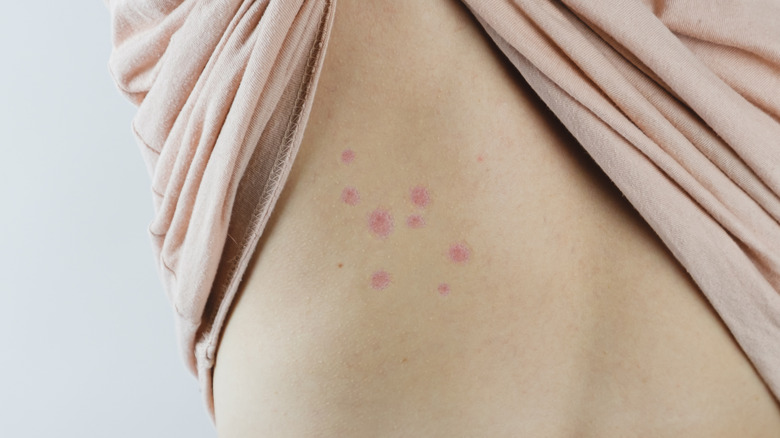
Bed bugs commonly strike while people are asleep by crawling out of their hiding area and onto the skin. They feed on blood for up to 10 minutes before returning to hiding. Since the bites go unnoticed until they begin itching — often, sometime later — people may not notice them until they awaken. Bites usually occur on areas uncovered during sleep, such as the neck, face, arms, and legs, and appear as small itchy red bumps with dark or clear centers (per Medical News Today). Unfortunately, the best way to confirm bed bug bites is to find the bed bugs (via WebMD).
Most bed bug bites heal on their own
To find bed bugs, you need to look for signs such as corpses or bugs in the sheets or mattress, rusty colored blood stains, or exoskeletons (per Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)). Once you know you have an infestation, you will likely have to contact pest control to eliminate the bugs using pesticides. Some bites can take 14 days to develop, so if you suspect bed bugs, it is best to try and seek them out sooner than later.
The bites themselves will likely appear as noticeable marks, causing itching, irritation, and swelling, according to Medical News Today. Most bites will heal within a week or two, but luckily, there are ways you can treat the symptoms. The first step in managing bites is to clean them thoroughly with soap and water. After the area is dry, you can apply anti-itch creams, hydrocortisone, or take oral antihistamines to reduce itching and swelling. If the reaction persists or is severe, you should seek medical attention, as an allergic reaction or infection can occur. In these severe cases, the medical professional may administer antibiotics, corticosteroids, epinephrine, or additional antihistamines after diagnosing the complication.
To prevent bed bugs at home, it is best to avoid buying used furniture from places like apartments that could be infested. Be sure to clean bedding regularly at high heat and vacuum upholstered areas frequently. When traveling, keep your luggage away from beds, furniture, and floors, and check hotel rooms immediately for signs of bed bugs.