What To Expect When Getting A DHEA Test
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) is a hormone produced by your adrenal glands, which are the small glands located on top of your kidneys. DHEA is a key hormone because it forms other important hormones, such as testosterone and estrogen, and also supports various other biological processes. Levels of DHEA peak around your mid-20s and then gradually decline with age, according to experts at Mayo Clinic.
Though produced in your adrenal glands, your brain is in charge of controlling the production of DHEA. For instance, when your system signals it is low in DHEA, your body uses a process called negative feedback that switches on the production of DHEA. Once your DHEA levels reach balanced levels, this feedback mechanism then switches off, per Endocrine Society.
DHEA is a vital precursor hormone because health experts believe it supports optimal health and well-being, with some published studies suggesting that DHEA may improve energy, libido, and other brain functions. Additionally, DHEA may play a role in reducing body fat, enhancing immunity, building muscle, and managing emotions, according to Harding Medical Institute.
Your DHEA levels decline over the course of your adulthood, diminishing to roughly 5% by the time you're 80. Because DHEA may also help decrease the risk of developing health issues such as cancer, heart disease, diabetes, obesity, dementia, and other serious conditions, some studies suggest that taking DHEA supplements may help decrease the chances of developing adverse health problems and may even prevent premature death, per Harding Medical Institute.
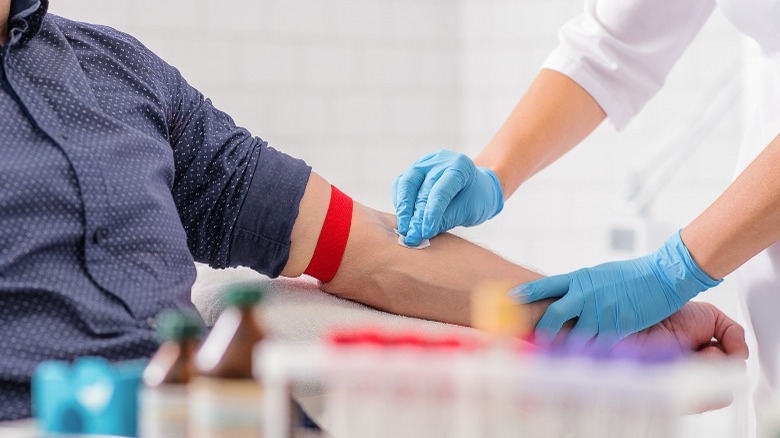
This is when you should get a DHEA test
Symptoms vary depending on whether DHEA levels are high or low. For instance, if you are a woman with high DHEA levels, the symptoms you may experience include irregular periods, hair loss, or vaginal atrophy in menopausal and postmenopausal women. Boys with high DHEA levels often go through early puberty. On the other hand, women with low DHEA levels may experience dizziness, dehydration, and nausea. Both women and men may also experience low libido, and men may develop erectile dysfunction, per Cleveland Clinic.
If you have symptoms, your doctor may order a DHEA sulfate (DHEAS) test, which can evaluate your hormone levels and assess potential health risks. A DHEAS test is a low-risk, simple test and does not require any preparation. Even so, you should notify your doctor about any medications you are currently taking, as some pharmaceuticals, vitamins, or supplements may impact DHEA levels. The DHEAS test involves your doctor or phlebotomist injecting a small needle into a vein in your arm to collect a small blood sample. Some patients may feel pain, throbbing, or bruising in and around the injection site, though these discomforts should recede fairly quickly, per Mount Sinai.
DHEA levels can vary depending on age, gender, overall health, and other factors. It's important to discuss the results of a DHEAS test with your doctor in the context of your general health, health history, and family history — along with any other relevant details, per UCLA Health.