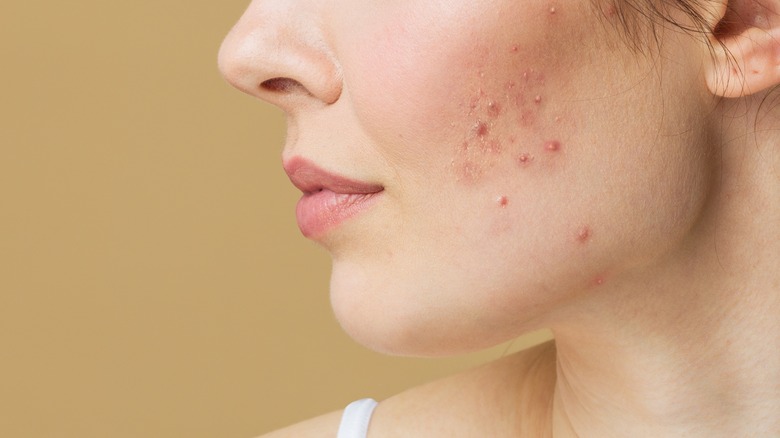
What Causes You To Have Fungal Acne?
Fungal acne, also known as Malassezia folliculitis, is a skin condition that results from an overgrowth of a yeast called Malassezia (via the Cleveland Clinic). This fungus is naturally found on the skin; however, when it gets stuck inside hair follicles, it can lead to pimples.
Regular acne and fungal acne are two distinct skin conditions with similar symptoms, but are caused by different factors and require different treatments. Normal acne is caused by an overproduction of oil and bacteria, which can clog the pores, per the Cleveland Clinic. This can result in the formation of pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads. Normal acne is most commonly found on the face, chest, shoulders, and upper back, according to the Mayo Clinic.
On the other hand, Cleveland Clinic notes that fungal acne typically appears as small, red, pimple-like bumps that are often itchy and may cause a burning sensation. They often appear on the chin, forehead, neck, and upper arms.
Causes of fungal acne
Several factors can contribute to the development of fungal acne. Hot, humid environments can create an ideal environment for the growth of Malassezia, says Healthline. The heat and humidity can cause skin irritation, which can make the skin more susceptible to fungal infections, says WebMD. In some cases, inadequate hygiene is another contributing factor. For example, if you re-wear dirty clothes where fungal growth is present, your skin is vulnerable to infection.
According to the Cleveland Clinic, antibiotics can also disrupt the balance of bacteria on the skin and create an environment that is more favorable for the growth of Malassezia. Antibiotics can kill off the "good" bacteria that normally keep the yeast in check, allowing it to overgrow and cause an infection.
Fungal acne can also be triggered by various other factors, including frequent skin touching, certain medications, immune suppression, oil-based skincare products that can clog pores, and using a hot tub.
How is fungal acne diagnosed and treated?
To prevent future outbreaks, it is recommended to practice good hygiene by keeping your skin and clothes clean and wearing breathable clothing, especially when it's hot. If self-care measures are not effective, seek the advice of a dermatologist, who can provide a proper diagnosis and prescribe the most appropriate treatment plan.
Typically, dermatologists can diagnose fungal acne by its appearance, symptoms, and lack of response to traditional acne treatments. In some cases, differentiating between normal acne and fungal acne can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar. Fortunately, a dermatologist can perform a skin scraping test to confirm the presence of the fungus and make a proper diagnosis, per the Cleveland Clinic.
Fungal acne is treated with antifungal medications and lifestyle modifications. Topical medications, such as creams or shampoos containing ketoconazole or clotrimazole, can be used on the affected areas to kill the overgrown fungus. In other cases, oral antifungal medications, such as itraconazole or fluconazole, may be prescribed, according to Healthline.
Note that it may take several weeks for fungal acne to clear and that it is essential to use antifungal medications as prescribed and practice good skincare habits even after symptoms have resolved.