What Does It Mean When You Have A Sudden Drop In Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure measures the force of blood against the artery walls (via Mayo Clinic). Low blood pressure, also known as hypotension, is a condition in which the blood pressure falls below a certain range. The normal blood pressure reading is usually considered to be around 120/80 mmHg. In general, a blood pressure reading lower than 90/60 mmHg is considered low, explains Mayo Clinic.
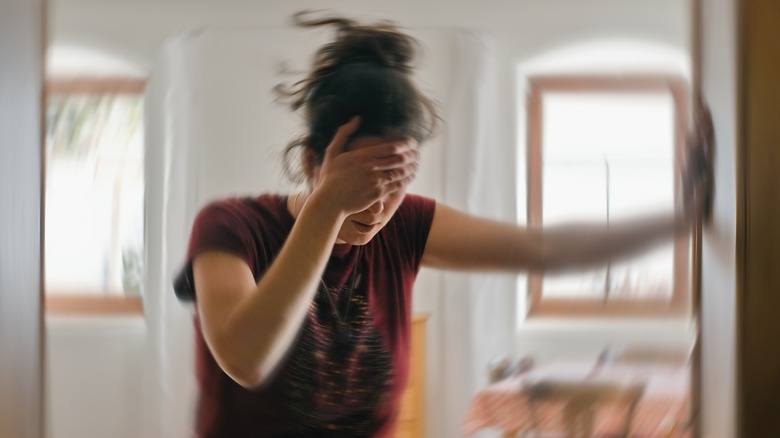
Symptoms of low blood pressure can include dizziness or lightheadedness, fainting, blurred vision, nausea, fatigue, rapid, shallow breathing, and trouble concentrating, says the clinic. It's important to note that not everyone with low blood pressure will experience symptoms, says the National Health Services (NHS). In some cases, low blood pressure may be discovered during routine blood pressure checks and may not cause any problems. However, if you experience symptoms of low blood pressure, it's important to speak with your doctor to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
What causes a sudden drop in blood pressure?
According to Healthline, dehydration is one common cause of a sudden drop in blood pressure. Dehydration occurs when the body does not have enough fluid and can cause your blood volume to drop, leading to a decrease in blood pressure, per Mayo Clinic. This can happen due to factors such as not drinking enough water, sweating heavily, or having diarrhea or vomiting (via Mayo Clinic).
Another common cause of sudden drops in blood pressure is low blood sugar, also known as hypoglycemia (via the Mayo Clinic). This can occur in people with diabetes who have taken too much insulin, missed a meal, or exercised more than usual.
In some cases, sudden drops in blood pressure can also be a symptom of a more serious underlying condition, such as septicemia, anemia, or a heart attack, says the clinic. If you experience symptoms of hypotension, it's important to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis and treatment of low blood pressure
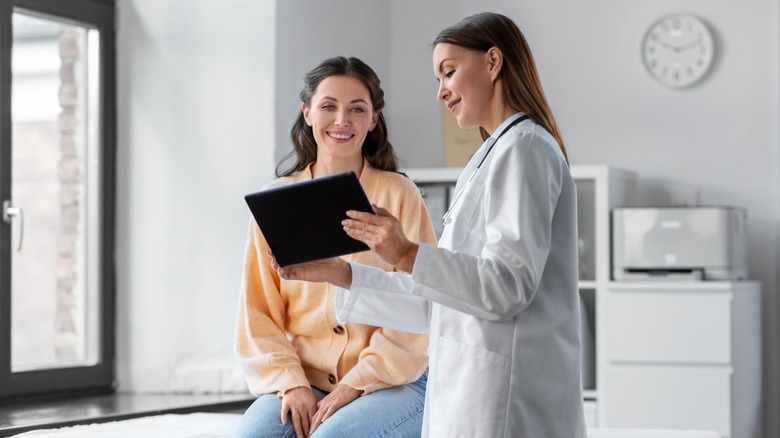
The diagnosis of low blood pressure typically begins with a medical history and physical examination. Your doctor might ask about your symptoms and any medical conditions you have and might also take your blood pressure to determine if it is low. In some cases, additional tests may be necessary to determine the underlying cause of your low blood pressure. These tests may include a complete blood count. In some cases, your doctor may also order an electrocardiogram (ECG) to evaluate your heart function, per Mayo Clinic.
The treatment of low blood pressure depends on the underlying cause. Following your doctor's recommendations and making any necessary lifestyle changes can help you manage your low blood pressure better. If the cause is due to a medication you are taking, your doctor may adjust the dose or switch you to a different medication. In some cases, lifestyle changes may help improve low blood pressure. This may include increasing your salt intake, drinking more water, exercising often, and limiting alcohol, advises WebMD.