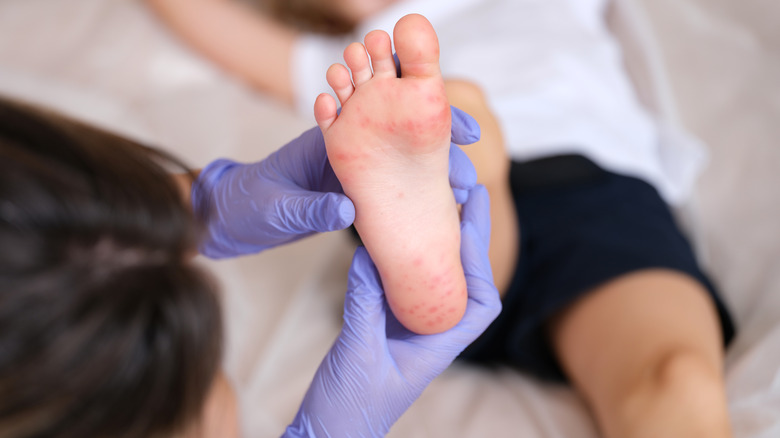
Can You Spread Cellulitis To Other People?
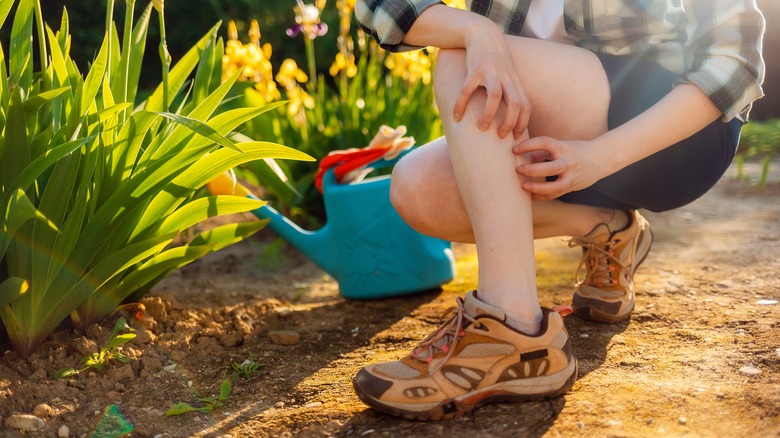
Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection that affects the deeper layers of the skin (via the Cleveland Clinic). It can occur anywhere on the body but most commonly affects the legs, feet, and toes. The infection is seen when bacteria, usually Staphylococcus or Streptococcus, enter the skin through a cut. The bacteria then spreads into the deeper layers of the skin, causing redness and swelling.
Cellulitis can affect anyone, but certain factors can increase the risk of developing the condition. These include having a weakened immune system, whether it was caused by leukemia, diabetes, or HIV/AIDS (per the Mayo Clinic). In addition, those having a skin condition like eczema or a history of lymphedema can also be more prone to cellulitis.
Symptoms of cellulitis include tenderness in the affected area, swelling, and pain. Sometimes, blisters may form on the skin, and the affected area may feel hot. However, in severe cases, the infection can spread to other body parts, leading to fever and chills.
Is cellulitis contagious?
Although cellulitis is normally caused by bacteria, it is not usually contagious, says the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The infection usually stays localized deep inside the affected area's skin and does not spread to other people, reiterates the NHS. While cellulitis is not typically contagious, it is still important to take precautions to prevent cellulitis from spreading deeper into the skin. In some cases, if the infection is not treated promptly or if the person has a weakened immune system, the bacteria can get into the bloodstream, leading to a condition called sepsis, which can be life-threatening.
If you suspect cellulitis, see a doctor as soon as possible for prompt treatment to prevent complications. Also, avoid touching or scratching the affected area to lessen the risk of infection. In addition, be sure to wash your hands frequently, especially after touching the affected area, and keep the area clean and dry.
How is cellulitis treated?
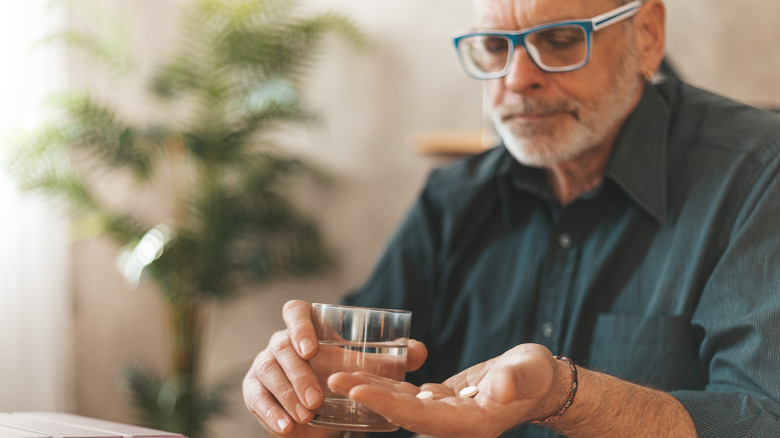
Cellulitis is typically treated with antibiotics to eliminate the bacterial infection, according to the experts at Mayo Clinic. The duration of treatment typically ranges from 5 to 10 days. However, the length of treatment may depend on the severity of the infection and the patient's response to treatment. For more severe cases of cellulitis, or if the patient doesn't respond to oral antibiotics, intravenous (IV) antibiotics may be necessary. This involves hospitalization, where the antibiotics are administered through a vein. This approach allows the antibiotics to reach the bloodstream more quickly and effectively.
In addition to antibiotics, treatment for cellulitis may include pain relievers. Nonetheless, rest, the elevation of the affected limb, and warm compresses may also be recommended to help reduce swelling and inflammation. All in all, follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider may also be necessary to monitor your progress and ensure the infection has been fully resolved.