Ozempic Explained: Uses, Dosage, And Side Effects
Ozempic (semaglutide), a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, has emerged as a promising treatment option for individuals with type 2 diabetes – a chronic metabolic disorder. This condition is characterized by the body's inability to properly utilize insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels, leading to prolonged high blood sugar levels and various health complications (via the Mayo Clinic).
In the United States, over 37 million people have been diagnosed with diabetes, with a staggering 90-95% of these cases being type 2, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). This highlights the critical need for safe and effective treatment options. Ozempic addresses this need by increasing insulin secretion and slowing gastric emptying, ultimately helping to control blood glucose levels. Additionally, Ozempic has been observed to aid in weight loss, making it a potentially attractive option for patients struggling with obesity-related diabetes.
Ozempic has recently garnered celebrity attention, which has heightened interest in its potential benefits and contributed to a drug shortage due to off-label claims of aiding in weight loss for the non-diabetic population (per Variety). Nonetheless, it remains crucial for patients and healthcare professionals to thoroughly understand Ozempic's uses, dosage, and potential side effects to ensure optimal treatment outcomes.
The science behind Ozempic
Ozempic, a prescription medication belonging to the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist class of drugs, is primarily used to manage type 2 diabetes (via Novomedlink). Its unique mechanism of action effectively regulates blood sugar levels while providing additional benefits, such as weight loss. Ozempic mimics the function of the body's natural GLP-1 hormone, essential for maintaining glucose stability. This hormone stimulates insulin secretion, inhibits glucagon release, and slows gastric emptying, contributing to a prolonged feeling of fullness.
In addition to promoting insulin release, Ozempic suppresses glucagon secretion from pancreatic alpha cells, preventing rapid blood sugar fluctuations. The drug also slows the rate of gastric emptying, which helps manage post-meal blood sugar spikes by allowing glucose to be absorbed more gradually into the bloodstream. This extended absorption process results in a longer period of satiety, contributing to weight loss for many patients (per Vox).
Ozempic's multifaceted approach to diabetes management makes it a valuable treatment option for individuals with type 2 diabetes. This combination of effects can lead to weight loss, further enhancing the health benefits for obese patients who use this medication as part of their diabetes management plan.
How is Ozempic prescribed?
Ozempic is typically prescribed for adult patients who require better glycemic control, especially when lifestyle modifications, such as diet, exercise, and other oral diabetic medications, have proven insufficient. Before prescribing Ozempic, healthcare providers must thoroughly evaluate a patient's medical history, current medications, and overall health to ensure the drug is appropriate for their specific needs.
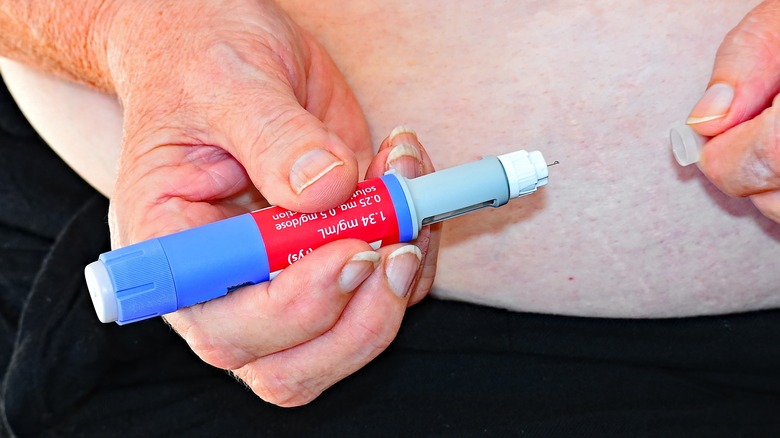
Ozempic is administered as a subcutaneous injection, usually once a week. The medication comes in prefilled pens with two dosage options — 0.5 milligram and 1 milligram. It is essential for patients to receive proper training on how to use the injection pen and dispose of used needles safely.
Healthcare providers typically start patients on a lower dose of Ozempic (0.25 milligram once weekly) for the first four weeks to minimize gastrointestinal side effects and allow the body to acclimate to the medication. After this initial period, the dose is typically increased to 0.5 milligram once weekly. If further glycemic control is necessary, the healthcare provider may consider increasing the dose to 1 milligram once weekly after an additional four weeks at the 0.5-milligram dose (via Ozempic).
In some cases, Ozempic may be prescribed with other diabetic medications to optimize blood sugar control. However, combining Ozempic with other medications may increase the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), so it is crucial for healthcare providers to adjust the treatment plan accordingly (per Mayo Clinic).
Essential tips for a smooth start with Ozempic
When taking Ozempic, following a few essential tips will help to ensure its effectiveness and minimize potential side effects. First, adhere to your healthcare provider's instructions regarding the dosage and frequency of Ozempic injections. Beginning with a lower dose and gradually increasing it as directed allows your body to adjust to the medication while minimizing gastrointestinal side effects.
Ozempic is administered as a subcutaneous injection once a week, so proper injection technique is critical. Your healthcare provider or pharmacist can advise you on how to use the prefilled injection pen correctly, rotate injection sites, and safely dispose of needles. Regular blood sugar monitoring is required to track the effectiveness of Ozempic and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment (via Ozempic).
Be aware of potential side effects and notify your healthcare provider if untoward symptoms persist or worsen. They may adjust your dosage or recommend additional measures to alleviate discomfort in some cases. Additionally, the manufacturer recommends combining Ozempic with a healthy diet and regular physical activity. This will improve your glycemic control and overall health. If maintaining a healthy diet feels challenging, consult a nutritionist or diabetes educator about developing a customized meal plan that aligns with your unique needs and preferences. Lastly, because Ozempic can slow gastric emptying, staying hydrated is critical. Drinking plenty of water helps prevent dehydration, especially if suffering from gastrointestinal symptoms. Following these tips may help you tolerate the medication more effectively (via Novo Nordisk).
Off-label uses for Ozempic
Ozempic has gained attention for potential off-label uses beyond blood sugar regulation.
A study published in Frontiers of Medicine discussed one off-label use for treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and its more severe form, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). These conditions involve the accumulation of fat in the liver, which can lead to inflammation, fibrosis, and, ultimately, liver cirrhosis or failure. Studies have shown that GLP-1 receptor agonists like Ozempic may help reduce liver fat content and inflammation, making them a potential treatment option for patients. However, more research is needed to confirm the efficacy and safety of Ozempic in treating these liver conditions.
Another potential off-label use for Ozempic is in the management of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a hormonal disorder affecting women of reproductive age. PCOS is often associated with insulin resistance, which can exacerbate hormonal imbalances and increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes (via PCOSWeightloss). As Ozempic improves insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, it may benefit women with PCOS who struggle with insulin resistance. Further studies are required to determine the effectiveness of Ozempic in treating PCOS and its long-term safety in this patient population.
Off-label use of medications should always be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional who can assess the potential benefits and risks in each case. While some studies have shown promising results for off-label use, further research is needed to establish its efficacy and safety.
Ozempic's role in weight loss management
The weight loss landscape is constantly changing as new approaches and solutions continue to emerge. Recently, Ozempic has captured the attention of health enthusiasts and medical professionals due to its unexpected impact on weight loss.
According to the American Council on Science and Health, Ozempic's promise for weight management stems from its ability to mimic the effects of the GLP-1 hormone. This hormone plays a crucial role in regulating appetite and blood sugar levels. With Ozempic, individuals may experience reduced hunger and better control of their blood sugar levels, ultimately leading to weight loss.
It is crucial to mention that a study published in Diabetes, Obesity, and Metabolism revealed that patients regained approximately two-thirds of the weight they lost once they discontinued using Ozempic. This finding raises concerns about the long-term effectiveness and sustainability of weight loss achieved through Ozempic, as regaining lost weight can negate the health benefits and potentially lead to a cycle of weight fluctuations.
While Ozempic offers a new perspective on weight loss management, it is not FDA-approved for weight loss at this time (via Healthline). Therefore, it is necessary to consult with your healthcare provider to determine if Ozempic is suitable.
Navigating common Ozempic side effects
Ozempic can sometimes cause side effects, but with appropriate knowledge and management techniques, you can mitigate their impact on your daily life. Being aware of common side effects and adopting proactive strategies can help you maintain a positive treatment experience.
Gastrointestinal issues, such as nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain, are among the most prevalent side effects of Ozempic (via WebMD). To manage these symptoms, your healthcare provider will start with a low dose and gradually increase it as your body adapts. Eating smaller, more frequent meals and avoiding high-fat or spicy foods may also provide relief. If these symptoms persist or worsen, contact your healthcare provider, as this could indicate a more severe condition such as pancreatitis or gall bladder concerns.
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, is another potential side effect, mainly when Ozempic is used alongside other diabetes medications (per Healthline). Regular blood sugar monitoring, adjusting your medication regimen, and consuming balanced meals can help prevent hypoglycemia. Keep a source of fast-acting sugar, such as glucose tablets or fruit juice, on hand in case of emergencies.
Furthermore, some patients may experience injection site reactions, such as redness, swelling, or pain. To minimize these occurrences, rotate injection sites and practice proper injection techniques.
Dietary considerations: Foods to avoid for optimal outcomes
Attention to your diet is essential when taking Ozempic, as certain foods can exacerbate side effects or interfere with the medication's effectiveness. Avoiding specific food items and making informed dietary choices can enhance your treatment outcomes and overall well-being.
Avoid high-fat meals, as they can worsen gastrointestinal side effects associated with Ozempic, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Instead, opt for lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil (via Diabetes Strong). Since Ozempic aims to regulate blood sugar levels, limiting foods high in sugar or simple carbohydrates is crucial. Cut back on sweets, sodas, and refined grains, focusing on incorporating complex carbohydrates from sources like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
Large meals can aggravate gastrointestinal side effects, making it more challenging to manage symptoms. To mitigate this issue, try eating smaller, more frequent meals daily to maintain steady blood sugar levels and reduce gastrointestinal discomfort. Additionally, alcohol consumption can increase the risk of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) and exacerbate gastrointestinal side effects; thus, it is advisable to limit your alcohol intake or avoid it altogether while taking Ozempic (per Medical News Today). Adhering to these dietary recommendations can support your Ozempic treatment for more successful diabetes management.
Who should avoid Ozempic treatment
While Ozempic is an effective medication for managing type 2 diabetes, it may not be suitable for everyone. Specific individuals should avoid using Ozempic due to potential health risks or complications. Understanding these contraindications can help ensure this medication's safe and appropriate use.
Ozempic is designed explicitly for treating type 2 diabetes, and is not approved for use in individuals with type 1 diabetes or diabetic ketoacidosis. Patients with a history of pancreatitis or gallbladder problems should exercise caution when considering Ozempic, as it may increase the risk of these conditions. Consult your healthcare provider to evaluate your suitability for this medication. Furthermore, WebMD reports that Ozempic is contraindicated for individuals with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2). This medication may elevate the risk of thyroid tumors, making it unsafe for these patients.
Additionally, a study published in Kidney Medicine determined that patients with severe kidney disease or those receiving dialysis might not be suitable candidates for Ozempic treatment. Discussing your medical history and potential concerns with your healthcare provider is crucial to determine the best course of action for managing your diabetes effectively and safely.
Social media's role in shaping a medication sensation
The buzz around Ozempic has reached a fever pitch on social media, with influencers, celebrities, and everyday users singing its praises. The contagious enthusiasm has even sparked concerns over a possible drug shortage due to the skyrocketing demand. As reported by USA Today, prominent celebrities like Elon Musk endorse Ozempic's benefits. These influential personalities, who have witnessed the drug's positive impact, contribute to the growing excitement surrounding Ozempic.
Novo Nordisk, the pharmaceutical powerhouse responsible for Ozempic, has skillfully harnessed the power of social media to boost its marketing campaigns. They have effectively attracted a wider audience by partnering with influential individuals and connecting with users through compelling narratives. The hashtag #Ozempic has amassed over 270 million views on TikTok, as the drug's reputation for promoting weight loss has earned it the title of a "miracle" medication (via ABC News).
However, the fear of a drug shortage looms large. While Novo Nordisk has ramped up production and strengthened supply chains, temporary shortages in some regions may still occur due to global supply chain disruptions and regulatory approvals (via Los Angeles Times).
Despite the social media hype playing a role in Ozempic's soaring popularity, its efficacy and safety drive its demand. In this viral age of digital word-of-mouth, the Ozempic craze serves as a reminder that social media can be a powerful tool for raising awareness about life-changing medications. Still, it is crucial to strike a balance between hype and reality.
Navigating Ozempic's cost and insurance coverage
The cost of Ozempic and its coverage by insurance can be significant factors when considering this medication for type 2 diabetes management. The retail price of Ozempic varies depending on the dosage, location, and pharmacy; however, it generally ranges from $800 to $1,000 per month for a 2-milligram dose(via Novocare). This high price tag may be daunting for many individuals, especially those needing insurance or have limited coverage.
Thankfully, most private and public insurance plans, including Medicare and Medicaid, offer coverage for Ozempic, which can help substantially reduce out-of-pocket expenses for patients. The level of coverage will differ depending on the specific insurance plan and any associated deductibles or co-payments. It is essential for individuals considering Ozempic to consult with their insurance provider to determine the exact level of coverage and any associated costs.
In addition to insurance coverage, there are other ways to make Ozempic more affordable. Novo Nordisk, the manufacturer of Ozempic, provides a savings card program for eligible patients, which can significantly reduce or even eliminate the cost of the medication for a limited time (per Ozempic). Moreover, patient assistance programs are available for uninsured or underinsured individuals, helping make the drug more accessible to those in need.
Understanding the implications when discontinuing Ozempic
When considering discontinuing Ozempic, it is essential to understand the potential implications of stopping the medication. As a GLP-1 receptor agonist, Ozempic plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels, promoting insulin secretion, and slowing gastric emptying for those with type 2 diabetes. When patients stop taking Ozempic, they may experience several changes in their diabetes management and overall health (per Ozempic).
First, for individuals using Ozempic primarily for diabetes management, discontinuing the medication may result in elevated blood glucose levels due to losing its blood sugar-regulating benefits. This increase in blood glucose can result in a heightened risk of diabetes-related complications such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and cardiovascular issues. It is crucial to closely monitor blood sugar levels and work with a healthcare professional to adjust other diabetes management strategies accordingly (via BuzzFeed News).
Additionally, some patients who have experienced weight loss while using Ozempic may notice a reversal of this trend after discontinuing the medication (per People). Weight gain is a common concern for individuals with type 2 diabetes, as it can contribute to insulin resistance and exacerbate the condition. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular physical activity, is essential to help counteract potential weight gain after stopping Ozempic. Lastly, when considering discontinuing Ozempic, it is vital to consult a healthcare professional to discuss alternative treatment options and develop a comprehensive plan to manage diabetes without the medication.