What Is DHT (And Signs You May Have Too Much In Your System)
If you've ever taken an Introduction to Biology course or read up on reproductive health, you might know that testosterone is the most recognized male sex hormone and estrogen is the most commonly known female sex hormone, despite each sex having both hormones. However, you may be less familiar with an equally important form of testosterone, dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
DHT is classified as an androgen hormone because it triggers the growth of physical characteristics stereotypically associated with the male sex, according to Cleveland Clinic. As a fetus grows, DHT plays a role in the development of the penis and scrotum. As described in a 2023 article published in StatPearls, DHT works with testosterone and anti-mullerian hormone (AMH) to prevent the growth of the female reproductive system.
In males, testosterone is converted into DHT in the testes and prostate, as explained by You and Your Hormones. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are the parts of the brain associated with regulating testosterone. The body produces more DHT when testosterone levels are high, and approximately 10% of testosterone is converted into DHT every day.
DHT can have stronger effects on the body than testosterone, which can lead to physical changes. It's believed that a rise in DHT levels may trigger puberty in boys and influence sexual behavior. In females, testosterone can be converted into DHT in the ovaries, which contributes to pubic hair growth during puberty. DHT can also be produced in other parts of the body, including the skin and liver.
Signs of too much DHT in your system
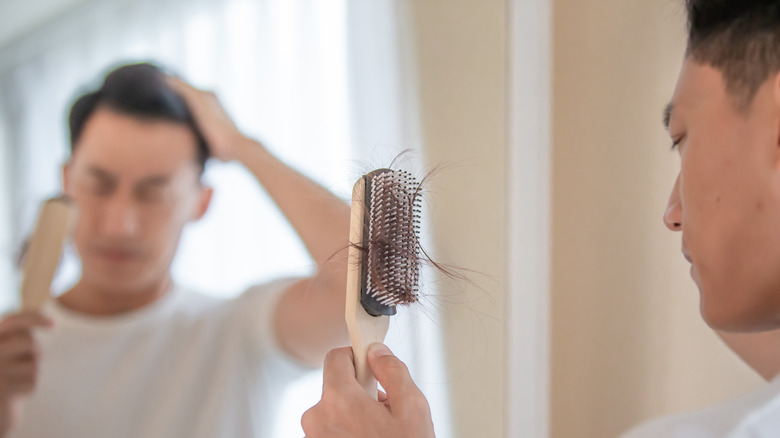
A hormonal imbalance of DHT can lead to problems for both men and women. In particular, elevated levels of DHT are thought to contribute to male-pattern baldness and hair loss by shrinking hair follicles on the scalp, as described by DrFormulas. Male-pattern baldness that stems from DHT overproduction will begin at the top of the head before progressing to the hairline. Women can also experience female pattern hair loss when their DHT levels are too high, so hair loss is a sign to look out for when assessing how much DHT is in your system.
Along with significant hair loss, high levels of DHT can make the prostate grow, as reported by Healthline. It's been hypothesized that too much DHT may be associated with prostate cancer, coronary heart disease, and slower recovery from injury. Too much DHT can also lead to sexual dysfunction and urinary problems in individuals experiencing prostate growth, according to Cleveland Clinic.
The presence of testosterone, and therefore DHT, is most prevalent in men. However, women with too much DHT in their body can also experience adverse effects. For example, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) may be associated with higher DHT levels. Because the ovaries are producing too many androgens, women with elevated DHT can have irregular periods, abnormal hair growth, and acne. One 2015 study published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism found that participants with PCOS had significantly higher DHT levels than participants without the condition.
Ways to lower your DHT levels
An overabundance of DHT can contribute to unpleasant symptoms, but there may be ways to get your hormones on the right track. DHT is a product of testosterone, so lowering DHT in the body may also mean modifying testosterone levels, according to BensNaturalHealth. For individuals with high levels of DHT, medication can suppress the enzyme responsible for turning testosterone into DHT. These medications can be used to treat hair loss and prostate growth related to excess DHT. However, DHT blocking medications may come with side effects, as Healthline notes.
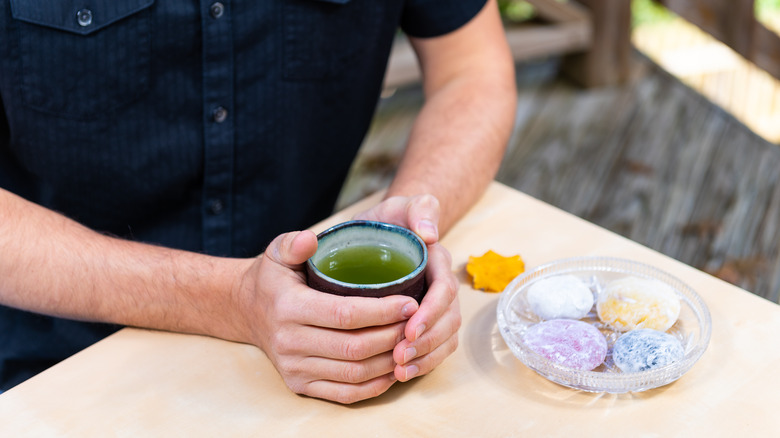
There are natural ways you can decrease the amount of DHT in your system. For example, you can consume more foods containing phytosterol or lycopene, which will naturally inhibit DHT production, as explained by Birmingham Dermatology Clinic. Some foods that serve as natural DHT blockers are spinach, carrots, kale, tomatoes, and watermelons. Those interested in herbal medicine could also try lowering their DHT levels with spring nettle, green tea, and saw palmetto.
Pumpkin seed oil may also benefit some people affected by hair loss from high DHT levels in the body. A 2014 study published in Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found that participants with male-pattern baldness had a 40% increase in hair growth after consuming pumpkin seed oil for 24 weeks.
If you're experiencing symptoms of elevated DHT levels, be sure to reach out to your primary care doctor for advice on what to do next.