What Is A Torn Cornea? Common Causes & Side Effects Of The Painful Condition
The cornea, the transparent, dome-shaped outer layer of the eye, plays several important roles in eye health. It covers the iris (the colored part of the eye) and the pupil (the black dot in the center of the iris where light enters the eye), shielding the inner eye from environmental hazards. It also allows light to enter the eye and directs it toward the retina, the part of your eye that turns light into signals that the brain interprets as vision. Without a properly shaped cornea, your vision will not be clear.
You might take your corneas for granted unless you have a problem with them, however. One such problem is a torn cornea, also known as a corneal laceration. A torn cornea is a deeper injury to the cornea that may involve a partial or full-thickness tear or cut. It is more serious than a corneal abrasion, which only affects the surface of the eye. In July 2025, Attorney General Pam Bondi experienced a torn cornea, which cast more attention to the condition as it kept her from fulfilling a speaking engagement.
Common causes of a torn cornea
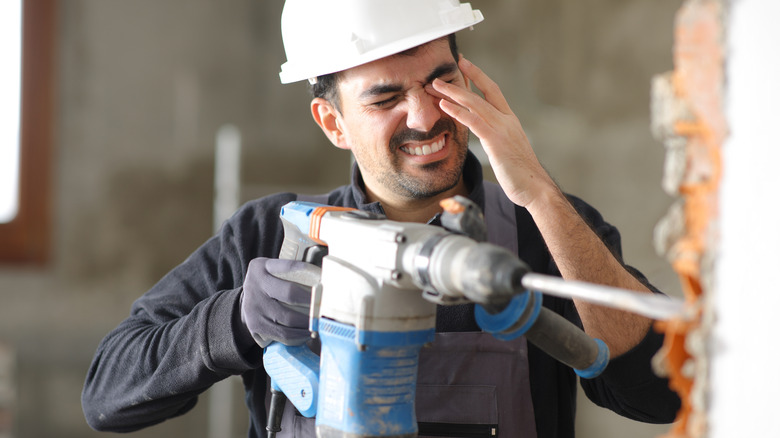
While the cause of Pam Bondi's torn cornea wasn't disclosed, there are a number of ways it can happen. For starters, a torn cornea often results from trauma caused by sharp objects or significant impact to the eye. This type of injury commonly occurs when small, high-speed objects fly into the eye, such as metal shards or wood splinters. Jobs and hobbies involving cutting wood, grinding metal, trimming grass with power tools, or carving stone present a high risk of such accidents. Even seemingly minor contacts — like dust particles, dirt, sand, or the sharp edge of a piece of paper — can cause a corneal cut if the force is sufficient.
The severity of the injury can vary, but deep lacerations may penetrate the full thickness of the cornea, potentially causing a ruptured globe, which is a tear that extends through the entire eyeball. This is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention to avoid permanent vision loss. To reduce the risk of these injuries, wearing protective eyewear during all hazardous activities is strongly recommended.
Signs and symptoms of a torn cornea
A torn cornea can cause a wide range of symptoms depending on the depth of the injury. Common signs include sharp, persistent eye pain; excessive tearing; and sensitivity to light (photophobia). Individuals may also experience blurry vision, redness, and a sensation that something is in the eye. In more severe cases, symptoms may include significant vision loss, irregularly shaped pupils, bleeding within the eye (hyphema), and corneal cloudiness. Some people report double vision, especially if swelling affects how light enters the eye. Deep lacerations may lead to iris tissue protruding through the wound and cause nausea or headache.
If you are having these symptoms and suspect that you have a torn cornea, Insight Vision Center Optometry advises that you seek immediate medical attention. Also, do not attempt to rinse your eye, remove any object stuck in it, or apply pressure. Instead, gently place a protective shield over the eye — such as the bottom of a paper cup — without pressing on it. Tape it loosely in place to prevent further injury. Avoid taking aspirin or other NSAIDs, which may increase bleeding. Prompt evaluation by an eye care professional is critical to preserving vision and preventing complications.