Why Getting A Tattoo Removed Is Riskier Than You Think
The popularity of tattoos has risen in recent years, with about 25% of the U.S. population having at least one, according to the Cleveland Clinic. Over time and with changing circumstances, sometimes people opt for tattoo removal. Fortunately, should you decide you no longer wish to have one, there are ways to safely restore your skin to its previous state.
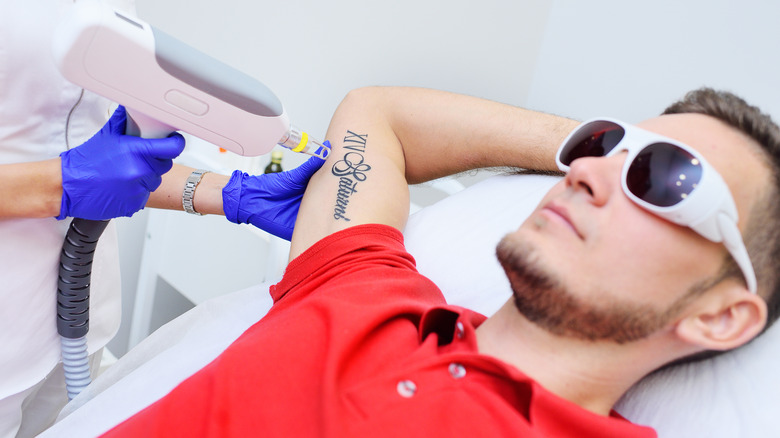
According to the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery (ASDS), there are three effective methods for removing a tattoo. One option is dermabrasion, a "sanding" down procedure to remove the skin on which the tattoo appears. After the procedure, skin often looks and feels more even and rejuvenated. Alternatively, laser surgery, which has become a popular method of treatment, involves the use of "high-intensity laser beams that break up the pigment colors and remove the tattoo." Finally, smaller tattoos can be removed by surgical excision. This is a more invasive method in which the tattoo is removed with a scalpel and the area is repaired with stitches. Large tattoos cannot be removed by this method.
The risks involved in tattoo removal
Any type of tattoo removal should be performed by a dermatologic surgeon (via American Society for Dermatologic Surgery). Never try to remove a tattoo by yourself. Tattoo removal at a salon or tattoo parlor may be safer than an at-home remedy, but it is not without risks. While going to a reputable healthcare professional will minimize these risks, there are still some things to keep in mind before making your decision.
According to the U.S. Food & Drug Administration, side effects of tattoo removal can include bleeding, redness, and soreness. These side effects typically do not last long and are expected to go away shortly after the procedure. The site of your tattoo removal is also at risk for infection and scarring. In some cases, scarring can develop three to six months after the procedure. Another possible side effect of tattoo removal is skin discoloration. The treated skin may become paler, known as hypopigmentation, or darker, called hyperpigmentation. If you have any concerns about the removal of a tattoo, talk to your doctor, or use the ASDS website to find a dermatologic surgeon who specializes in tattoo removal.