What Are Shin Splints And How Can You Treat Them?
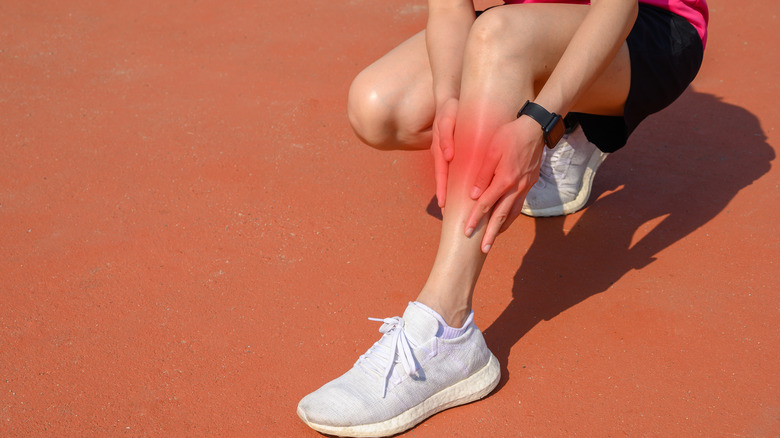
Shin splints are a common athletic injury that causes pain along the edge of the shin bone, or tibia. Also known as medial tibial stress syndrome, shin splints occur when the muscles and tendons in your lower leg pull on the shin bone and become irritated and inflamed (via Healthline). This is often caused by overuse and repeated stress on the shin bone and the surrounding muscles and connective tissues. Although anyone can get them, shin splints are most common among runners, athletes, military recruits, and dancers. People with flat feet and rigid arches are also more likely to develop shin splints.
Shin splints can be quite painful, especially when they are not given the time needed to fully heal, which can make it difficult to walk or exercise. In addition to the pain along the outer edge of the shin bone, shin splints can also cause pain, tenderness, and soreness along the front and inner part of the lower leg, numbness and weakness in the feet, and mild swelling in the lower leg.
How to treat shin splints
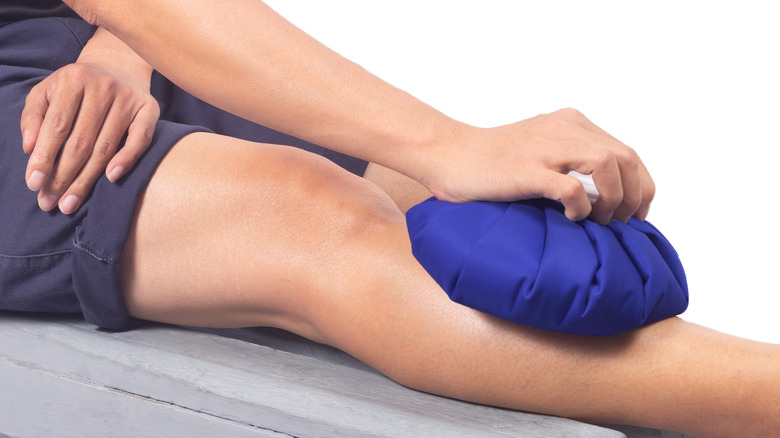
If you're experiencing painful shin splints, there are a few things you can do to help treat the condition and alleviate discomfort from symptoms. First and foremost, you need to rest and give yourself time to heal (via Cleveland Clinic). The most important thing you can do is stop exercising for a few weeks until the pain subsides. During this rest period, you can treat your symptoms with ice and pain relievers until you fully recover. You can do this by applying ice or an ice pack to your shins for 20 minutes at a time. This will help reduce any swelling and pain.
You can also take over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen and naproxen to help relieve pain in your shins. In addition, wearing the right footwear can make all the difference. Inserts and shoes with orthotic support can help relieve any stress and pressure that you may be putting on your shin bones. Wearing supportive footwear is especially helpful for people with high arches or flat feet.