How Serious Is A Collapsed Lung?
A collapsed lung, or pneumothorax, happens when air leaks into the space between your lung and chest wall. This is known as the pleural space (via Cleveland Clinic). The pressure of this air in the pleural space can build up and push against the outside of your lung, causing it to either fully or partially collapse. This can lead to shortness of breath, chest pain, cough, fatigue, rapid heart rate, fast breathing, and blue-colored skin.
A collapsed lung can be caused by many different factors, including an injury to the lung and chest wall. This is often the result of a fractured rib, certain medical procedures, or a gunshot or knife wound to the chest. It can also be caused by lung disease. Conditions like cystic fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and emphysema can all increase the risk of developing pneumothorax. However, sometimes a collapsed lung can occur spontaneously and seemingly without cause. This can occur as a result of air sacs that form in the lungs and release air when they burst.
A collapsed lung can be life-threatening
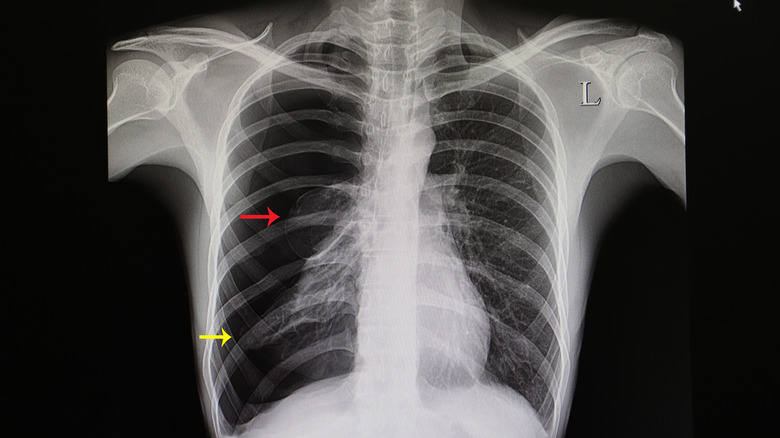
While rare, a collapsed lung can be quite serious. In some cases, it can even be fatal. That's why it's important to seek immediate medical attention if you're experiencing symptoms of a collapsed lung (via Medical News Today). Your doctor or medical provider will physically examine you and evaluate your symptoms in order to determine a proper diagnosis. They may take CT scans and X-ray images of your chest to look for signs of a pneumothorax. The exact treatment will depend on the severity of the problem.
Treatment for a collapsed lung can include draining excess air from the pleural space, supplemental oxygen, and surgery. Depending on the damage, some people will heal without treatment, while others require emergency medical attention. People who have underlying lung conditions are at a greater risk of further complications and even death. If you're having trouble breathing and are experiencing sharp pains in your chest, you should seek emergency medical care.