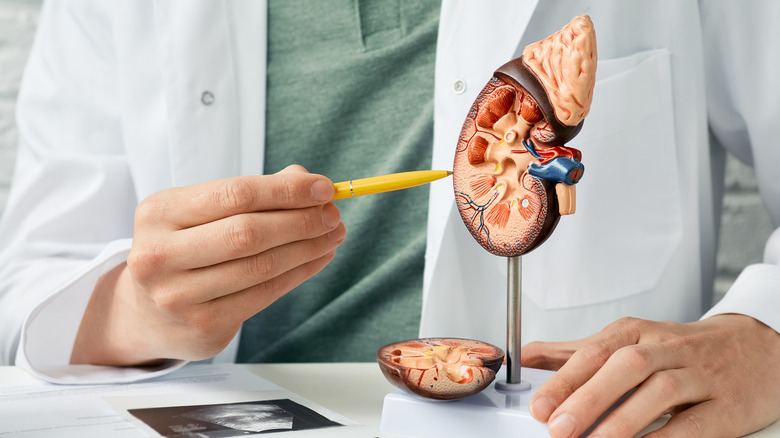
What's The Difference Between Acute Kidney Injury And Chronic Kidney Disease?
Acute kidney injury (AKI) and chronic kidney disease (CKD) are two different conditions that affect the kidneys. AKI is defined as a rapid decline in kidney function, usually associated with some underlying condition such as sepsis or dehydration. CKD, on the other hand, is a long-term condition characterized by slowly declining kidney function over time (via Verywell Health). The treatments of these conditions are different, so it is important to know as much as you can about both diseases if you have any of the symptoms.
The main difference between AKI and CKD is the speed at which they affect the kidneys. In patients with AKI, symptoms typically develop rapidly and can be severe, while patients with CKD may not experience any symptoms until their kidneys have already been damaged significantly. Additionally, treatment options for patients with AKI are often more aggressive than those for patients with CKD.
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a serious health problem that can occur at any time. It's most commonly caused by infection, dehydration, or medications. In some cases, AKI is the result of another underlying medical condition. Precisely what causes AKI depends on whether the problem occurs in the kidneys themselves (intrinsic AKI), above them (prerenal AKI), or below them (postrenal AKI). The most common symptom of AKI is a sudden decrease in urine output. Other symptoms may include swelling in the feet, legs, or ankles, abdominal pain or bloating, nausea and vomiting, shortness of breath, fatigue, or weakness.
What to know about chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a condition that gradually worsens over time and involves the gradual loss of kidney function (via Medical News Today). This can happen over the course of months or years, although in some cases it happens more quickly. There are many different causes of CKD, including diabetes, high blood pressure, and even certain medications. Other possible causes include injury to the kidneys from an infection or traumatic injury as well as certain genetic conditions.
Symptoms of chronic kidney disease may include fatigue, weakness, nausea, vomiting, frequent infections, bleeding easily, and changes in skin coloration. In advanced stages of CKD, the patient may experience swelling in their legs or ankles due to fluid retention. They may also have difficulty urinating and their urine may contain blood. Chronic kidney disease can eventually lead to kidney failure, which is when the kidneys are no longer able to function properly. This can be a life-threatening condition and requires dialysis or a kidney transplant to survive.
If you have any of the risk factors for chronic kidney disease or acute kidney failure, it's important to get checked by your doctor so that the condition can be diagnosed and treated early. Treatment options will vary depending on the underlying cause of the conditions and the stage of the disease. In some cases, treatment may only be necessary to manage symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. Sometimes more aggressive treatment may be necessary.