Reasons Why Your Tonsils Are Swollen
The tonsils are two round, bulky masses located in the back of the mouth, as the Cleveland Clinic explains. They're made of soft tissue similar to lymph nodes and are an essential part of the body's immune system. The tonsils make their own disease-fighting white blood cells, and since they're located in the back of the throat, they're strategically positioned to help fight and prevent germs.
The different types of tonsils are palatine, adenoids, and lingual, according to a 2019 article published in InformedHealth. Palatine tonsils are the most visible when you open your mouth, while the adenoids are positioned deeper and higher up in the throat, behind the nose. The third type, the lingual tonsil, is also located at the base of the tongue.
At times, inflammation or swelling of the tonsils can occur, making day-to-day living uncomfortable. In fact, there could be various reasons why your tonsils are swollen, and treatment will depend on the cause.
Tonsilitis
Tonsillitis occurs when your tonsils are infected, according to Medical News Today. The most common cause is a viral infection associated with rhinovirus, adenovirus, influenza, and respiratory syncytial virus. Other less common viral infections include herpes simplex and Epstein-Barr. Although a viral infection is the most common cause of tonsillitis, a streptococcus pyogenes bacterial infection can also inflame your tonsils.
Keep in mind, there are a number of factors that can determine why your tonsils are swollen. While anyone at any age can develop tonsillitis, some people are more susceptible. In a 2020 study published in the Journal of Pakistan Medical Association, 325 people were clinically diagnosed with tonsillitis. The study concluded that age, unhygienic living conditions, stress, and eating spicy foods were the most common risk factors.
Tonsillitis can range from acute to chronic, and the symptoms can be unpleasant, according to Healthline. Acute cases don't usually require treatment. However, be sure to see a doctor if your symptoms include breathing difficulties, fever, muscle stiffness, or a sore throat that lasts more than two days. In some cases, treatment for severe cases includes the use of antibiotics.
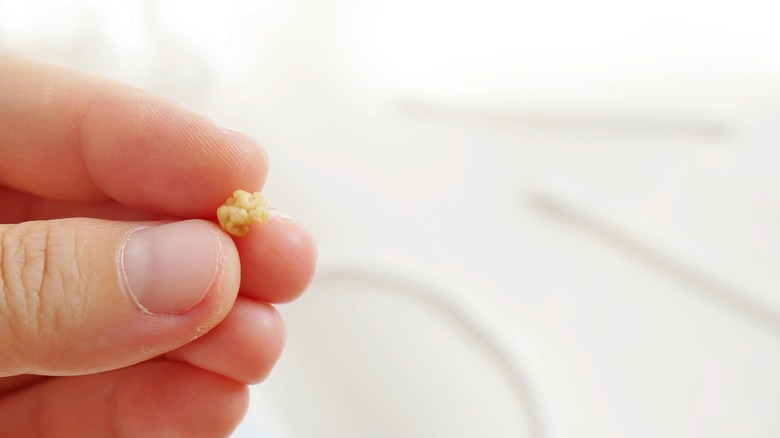
Tonsil stones
Tonsils naturally come with openings that present opportunities for bacteria and other harmful substances, like dead cells and mucus, to enter, explains WebMD. When these substances get trapped in your tonsils, they may harden or calcify, which forms a small stone-like appearance. These stones are likely to develop in people with long-term inflammation in their tonsils. Keep in mind, the stones usually become visible as they increase in size, often appearing as whitish or yellowish specks on your tonsils, as per Healthline.
While the exact manner of how tonsil stones are formed is unknown, risk factors include poor dental hygiene or underlying conditions, like chronic sinus issues and tonsillitis. Also, most cases of tonsil stones don't present symptoms. However, in symptomatic cases, you might experience swollen tonsils and bad breath since tonsil stones harbor anaerobic bacteria, which produce pungent sulfides, says Medical News Today. Besides inflamed tonsils and halitosis, you might also experience an irritating cough or a bad taste in the mouth. Luckily, treatment often includes at-home remedies. But if the stones are too large, your doctor might recommend a tonsillectomy — a surgery to remove the tonsils.
Strep throat
Strep throat is an infection that often stems from a bacteria called streptococcus (via the Cleveland Clinic). The condition is contagious and usually presents itself with a sore throat, per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The center estimates that in the United States, up to three in 10 children and one in 10 adults with a sore throat have strep throat, indicating that the condition is more common in children, especially between five and 15 years old. Keep in mind, the streptococcus virus can be transmitted through droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes, explains the Mayo Clinic. Therefore, you can easily develop the condition by touching door knobs and other surfaces, especially in the winter or early spring.
As for symptoms, strep throat can lead to red and swollen tonsils, among various other offshoot symptoms, like painful swallowing, throat pain, and headaches. It's best to see a doctor if you experience breathing difficulties for more than 48 hours. Treatment for strep throat often includes antibiotics, like amoxicillin, cefadroxil, and cephalexin, since a bacterial infection causes strep throat, notes Healthline.
Infectious mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis (mono), also known as the kissing disease, is a viral infection that spreads through saliva droplets, per the Mayo Clinic. You can get infected after kissing someone with the infection or drinking from the same glass. Infectious mononucleosis can cause your tonsils to soften and become swollen. Most people with the virus may experience other common symptoms, including fever, headaches, and fatigue. However, these symptoms may not show until about four to six weeks after exposure to the virus.
In fact, sometimes symptoms can seem to bear a similar resemblance to other health conditions, according to Johns Hopkins Medicine. Therefore, if you are unsure of what's causing the infection, it's best to consult your doctor. They usually diagnose the condition with a physical examination and might look for growths in your tonsils and check if you have a swollen liver or lymph nodes in the front or back of your neck (via Medline Plus).
Since a viral infection causes infectious mononucleosis, there's no specific treatment method, says the Mayo Clinic. On that account, your doctor can advise you to get some rest, eat healthily, and drink lots of fluids.
Tonsil cancer
Cancer can spread anywhere in the body, and your tonsils aren't an exemption. Tonsil cancer happens when healthy cells in the tonsils develop changes causing the cells to grow abnormally (via Mayo Clinic). The exact cause of tonsil cancer is unclear, but new scientific breakthroughs show a connection with human papillomavirus (HPV). This sexually transmitted infection has been detected in many cases of tonsil cancer. However, you might also be susceptible to tonsil cancer if you smoke tobacco or abuse alcohol.
Tonsil cancer can occur even if your tonsils are removed, since some tonsil tissues remain after surgery, according to Medical News Today. Keep in mind, tonsil cancers are mostly squamous cell carcinomas, while others are lymphomas.
One way to know if you have tonsil cancer is to see if one tonsil is larger than the other, according to the Cleveland Clinic. You might also feel as if something is stuck in your throat. Nevertheless, the condition can cause pain in your mouth, throat, and ears. Symptoms may not be obvious since they differ from one person to another. But if you already have enlarged tonsils, other common symptoms linked to tonsil cancer may include bad breath and difficulty swallowing or speaking.