Things You Didn't Know Could Affect Your Medication
Taking medication is a part of hundreds of millions of Americans' daily routines (via Georgetown University). And while many know that medicines can interact with each other, what people often don't realize is that food, drinks, supplements, and more can also have an impact on the medications we take. These interactions can change the effectiveness of the drug and sometimes can even have dangerous side effects. On top of all that, making sure to take your medications on time or properly spaced out is another important factor in the drug's ability to do its job.
When taking a new medication, first and foremost, it's always important to talk to your healthcare provider or pharmacist to see if there is anything you should avoid when taking it. And in case you aren't aware of what things — like foods and supplements — could be causing potentially harmful interactions, let's take a look.
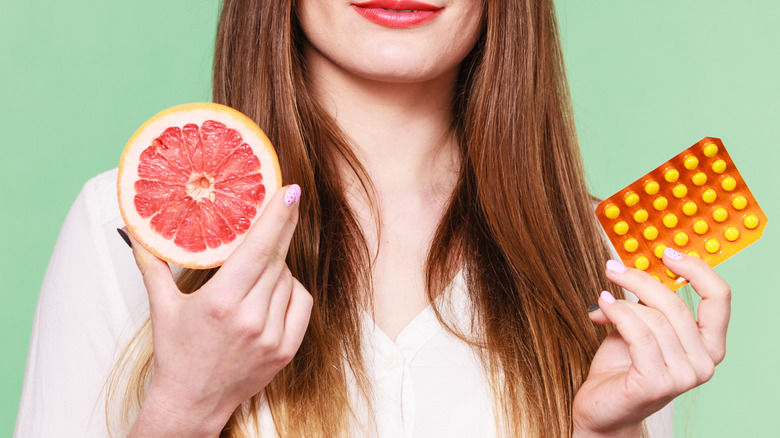
Grapefruits are notorious for having an impact on medications' effectiveness
Grapefruits are a great source of nutrients — they can benefit your immune system and they can improve heart health — but with all the positives of grapefruits, there are some risks to be aware of if you're taking medication. Grapefruits are notorious for impacting the way medicines work, especially if you have specific conditions like high blood pressure or arrhythmia.
So why do grapefruits interact with meds? Well, according to WebMD, grapefruits can change "the way certain cells in your gut take in and move medication through your body." And they can "affect more than 50 drugs." The outlet noted that citrus fruit can have a variety of impacts on medications, making some too weak and others too strong.
This is true of grapefruit juice as well. According to the U.S. Food & Drug Administration, "The severity of the interaction can be different depending on the person, the drug, and the amount of grapefruit juice you drink." So if you take prescription medication, make sure to double-check with your healthcare provider before eating grapefruit or drinking grapefruit juice.
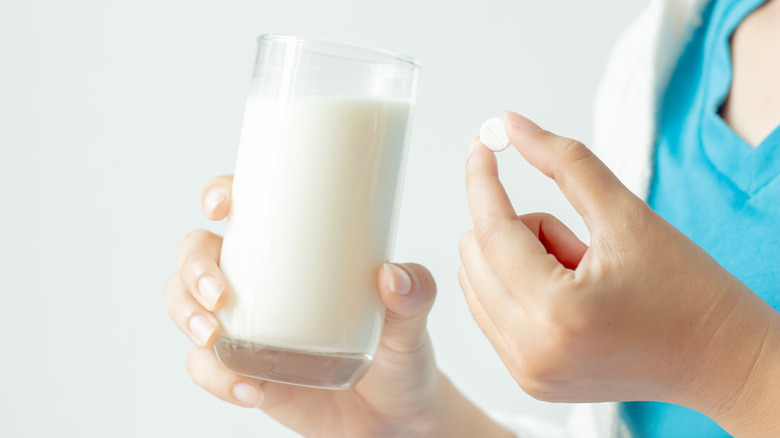
Milk and other dairy products can make antibiotics less effective
Milk is known to provide health benefits and nutrients like calcium, iron, and more. But some of those same nutrients can actually cause issues when mixed with certain medications. According to Pharmacy Times, dairy products can interfere including antibiotics such as tetracycline, doxycycline, and ciprofloxacin. The outlet reported, "These antibiotics may bind to the calcium in milk, forming an insoluble substance in the stomach and upper small intestine that the body is unable to absorb." This means that the dairy products could be making your antibiotics less effective.
In an article for Blanchard Valley Health System, physician's assistant Jacqueline Boucher agreed that dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese can decrease the absorption of antibiotics. To avoid dairy products impacting the effectiveness of the medication, she suggested, "Try to eat meals one to two hours before taking these to avoid this interaction." You don't have to avoid dairy altogether when taking antibiotics, just give your body some time to absorb them separately.
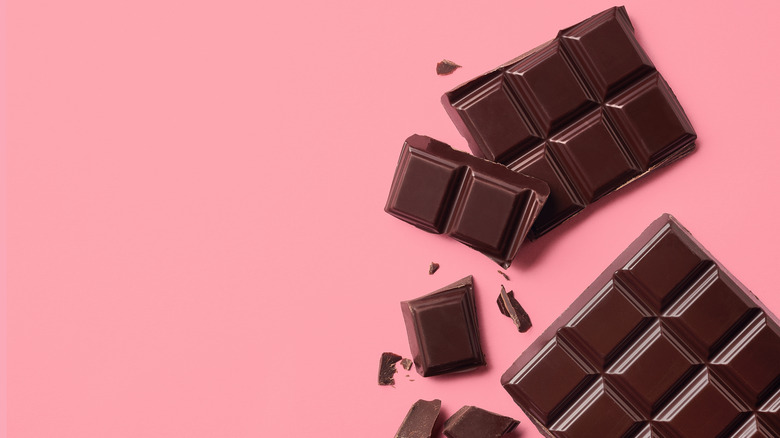
The caffeine in dark chocolate can interact with a variety of medications
Dark chocolate is not only delicious, but it is also a powerful source of antioxidants and it may reduce the risk of heart disease (via Healthline). But with all the benefits of dark chocolate, the U.S. Food & Drug Administration still lists it as one of the foods to watch out for when taking medication. Chocolate can interact with a variety of medications — and for a variety of reasons.
WebMD noted that the caffeine in chocolate, particularly dark chocolate, can dull the effects of Ambien and other drugs meant to help you sleep. And on the other hand, it can increase the potency of stimulants, like Ritalin. Mixing chocolate and monoamine oxidase inhibitors isn't a good idea either, as the depression medication can cause your blood pressure to become "dangerously high," WebMD explained.
"Consumers should learn about the warnings for their medications and talk with their health care professionals about how to lower the risk of interactions," Shiew-Mei Huang, deputy director of the Office of Clinical Pharmacology in FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, advised when speaking with the U.S. Food & Drug Administration.
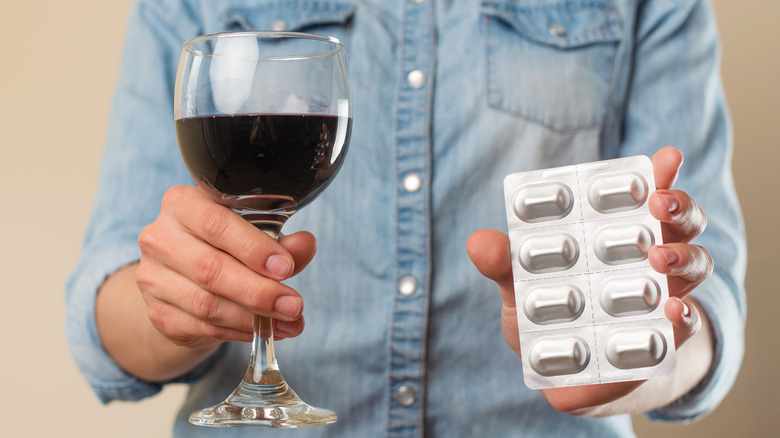
Combining alcohol with many medications can lead to dangerous health consequences
Many medications, including over-the-counter ones, come with a warning on the label about alcohol intake and interactions, but not everyone reads the labels or takes those suggestions seriously. A Northwestern University study also revealed that some patients have difficulty understanding medicine labels (via ScienceDaily).
According to Verywell Mind, drinking alcohol not only affects how your medications work, it can also be dangerous. "The combination can lead to serious health consequences, including overdose and even death," the site warned. And the list of drugs that can have negative interactions with alcohol is extremely lengthy. Alcohol can impact everything from flu medications to anxiety meds to antibiotics, to blood thinners, to sleep aids, and more.
Verywell Mind cautioned that you should learn how alcohol can impact the medications you take. Physician's assistant Jacqueline Boucher agrees. In an article for Blanchard Valley Health System, she explained that people must even be careful with medications like acetaminophen (Tylenol) "because it has a higher chance of causing severe liver damage."
Antihistamines can be problematic for people who have high blood pressure
When allergy season sets in, many people reach for over-the-counter antihistamine products like Allegra, Zyrtec, Benadryl, Claritin, and more. These can help provide relief for a runny nose, sneezing, itching, and watery eyes. But according to WellRx antihistamines, especially ones that are decongestants, can actually have a negative impact on people with high blood pressure or heart problems.
The outlet reports that medications like Allegra, Zyrtec, and Benadryl can alter the effectiveness of certain blood pressure medications. Additionally, the interaction can cause other unwanted symptoms like excessive drowsiness. WellRx suggests avoiding decongestants altogether if you have high blood pressure or heart problems. As the site explained, "Decongestants constrict (narrow) blood vessels to open nasal passages and facilitate breathing. Because decongestants constrict blood vessels throughout your body, they can worsen hypertension. Additionally, decongestants stimulate the release of norepinephrine in your body, which raises your blood pressure and your heart rate."
If you have seasonal allergies and also deal with high blood pressure or heart problems, there are other ways to get relief from allergies like acupuncture, saline sprays, and using air purifiers (via WebMD).
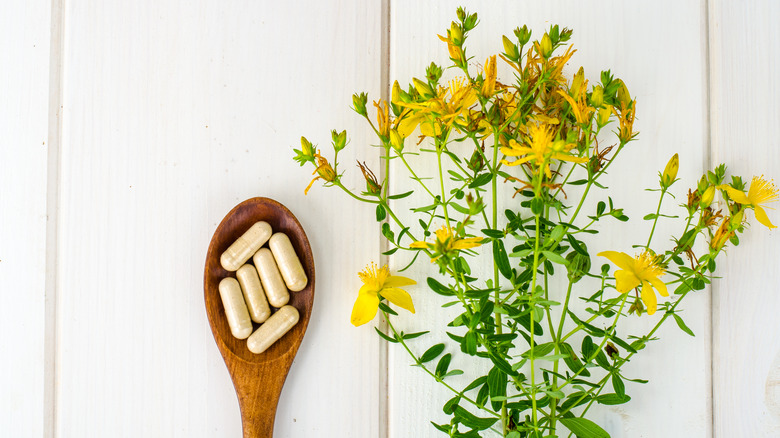
St. John's wort's list of interactions might outweigh the benefits
In case you haven't heard of St. John's wort, it's a plant with yellow flowers that has been used in traditional medicine as far back as the ancient Greeks. Mayo Clinic reported that St. John's wort is often used as an herbal remedy to help treat mental health problems like depression, menopausal symptoms, and somatic symptom disorder. And while this herbal remedy has evidence-based benefits, according to Mayo Clinic, "the supplement interacts with many medications and can cause serious side effects."
St. John's wort is notorious for interacting with other mental health medications like Xanax and antidepressants, but it also can impact the effectiveness of contraceptive drugs, antihistamines, heartburn medication, and more. And on top of St. John's wort making medications more or less effective, it can also come with side effects like stomach discomfort, insomnia, headache, photosensitivity, and more.
According to Mayo Clinic, "When taken orally for up to 12 weeks in appropriate doses, St. John's wort is generally considered safe." But if you take any other medications, you might want to explore other options as well, given all of St. John's Worts interactions. This is why it's always important to make sure to check with your healthcare provider before taking any new supplements, including herbal ones!
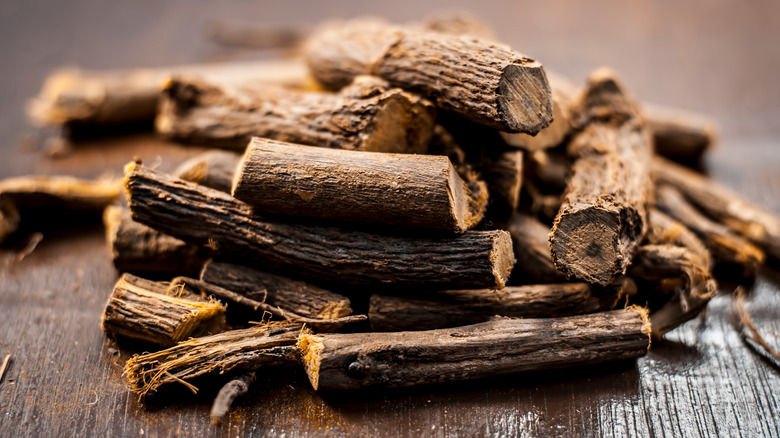
Licorice isn't just candy, it's an herb that can impact the effectiveness of many meds
While many people just think of licorice as the candy, many "licorice" products produced in the United States don't contain any licorice at all. Instead they contain anise oil, which smells and tastes like black licorice. But when it comes to the actual licorice herb, it actually has many health benefits. According to WebMD, "Some people use this as an herbal remedy to help with digestion, and others use it to flavor foods."
But when using licorice as an herbal remedy, it's important to consider what medications you're taking because like many other herbs, it can interact with a variety of drugs. WebMD reports that "glycyrrhizin, a chemical in licorice, can weaken the effect of some drugs, including cyclosporine, used to keep people who've had transplants from rejecting their new organs." It can also impact other medications like corticosteroids, diuretic drugs, and liver medications. So if you take any meds, it's important to talk to your healthcare provider before adding herbs like licorice to your daily routine. You want to make sure it doesn't interfere with any medications that you already take.
Taking medications at the wrong time can have serious side effects
When getting caught up with busy schedules and buzzing around, it's easy to forget to take your daily medications. This can unfortunately have a major effect on how the drugs work. According to WebMD, "Only about 50% of medication is taken as it's prescribed. People often take less than they need, take it at random times, or leave big gaps between doses — all of which can weaken the effects."
This can impact the effectiveness of a variety of drugs, like contraceptive pills and sleeping medications, but it can be even more serious for specific drugs like HIV medication. The HIV Clinic with Toronto General Hospital asserts that "medications should be taken regularly to make sure that you have an effective amount of drug in your body at all times." If they are not taken regularly, the clinic states that "the level of drug in the blood can become too low to effectively stop the virus from multiplying." This can let the virus mutate and become resistant to the effects of the drug.
It's extremely important to read the labels and check with your healthcare provider about how the timing of taking your medications can impact the effectiveness. And if you need to take your meds at the same time every day, try setting an alarm so you don't forget.
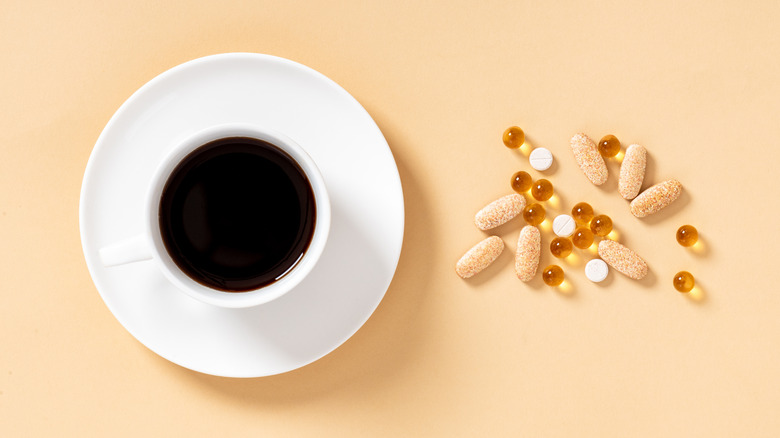
Coffee can reduce the absorption of certain medications
According to the National Coffee Association, 62% of Americans drink coffee every day and the average coffee drinker drinks just over 3 cups per day. But what coffee lovers might not realize is that coffee can impact the effectiveness of many medications. The New York Times reported that coffee can either block the absorption or increase the effects of some prescription drugs like antidepressants, antibiotics, and birth control pills.
"In many cases, the interactions are caused by caffeine. But other compounds in coffee may also play a role," according to their report. One study cited by the publication "found that people who drank coffee shortly before or after taking levothyroxine, a common thyroid medication, experienced a reduction of up to 55 percent in absorption of the drug." They also pointed to other studies that revealed how coffee can reduce the absorption of osteoporosis drugs and that "it can lower circulating levels of estrogen and other hormones in women." If you take medication talk to your healthcare provider before you reach for a cup of coffee to make sure it won't cause any unwanted interactions.
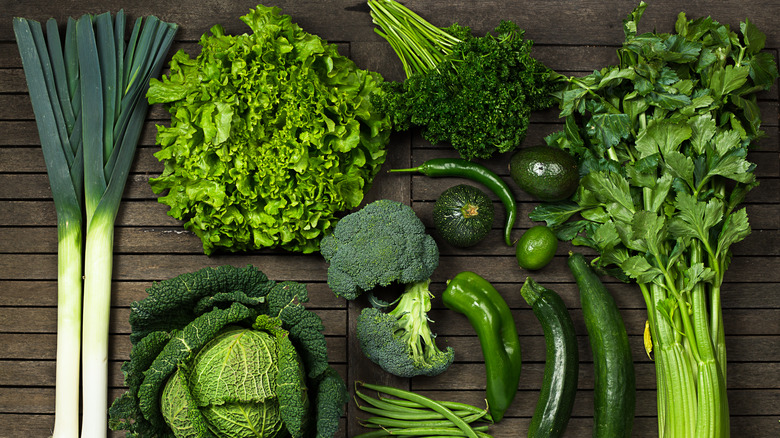
Green leafy vegetables can make blood thinners less effective
Dark leafy greens are packed with vitamins and are an essential part of a healthy, balanced diet. According to Healthline, eating leafy greens can afford you with "numerous health benefits including reduced risk of obesity, heart disease, high blood pressure and mental decline." But like many things, even something as healthy as green leafy vegetables can interact with certain medications.
In an article for Blanchard Valley Health System, physician's assistant Jacqueline Boucher revealed, "Green, leafy vegetables, which are high in vitamin K, can decrease how well aspirin thins the blood. Consuming the same amount of green-leafy vegetables each day will decrease this interaction." Veggies that are high in vitamin K include kale, collard greens, broccoli, spinach, cabbage, and lettuce.
If you take a medication used to treat blood clots, be aware of how much of these vitamin K-rich vegetables you take in. It can make the blood thinners less effective and put you at higher risk of a dangerous blood clot.
Iron supplements can impact the absorption of other medications
Iron is a mineral that our bodies need for growth and development and it's essential in helping transport oxygen throughout the body (via Office of Dietary Supplements). So when someone is deficient in iron, their healthcare provider will likely advise them to take an iron supplement to avoid the unwanted side effects of an iron deficiency. But before adding an iron supplement to your daily routine, it's important to know how it interacts with other meds you may be taking.
According to MedlinePlus, "Iron tablets may cause other drugs you are taking to not work as well. Some of these include tetracycline, penicillin, and ciprofloxacin and drugs used for hypothyroidism, Parkinson's disease, and seizures." Additionally, MedlinePlus reported that medications that reduce stomach acid, like Prilosec and Prevacid, can impair the absorption of iron.
In order to avoid altering the effectiveness of both your prescription medications and the iron supplements, wait two or more hours between doses of these drugs and iron supplements. And it's always important to check with your provider to make sure none of your other medications will interact with your supplements.
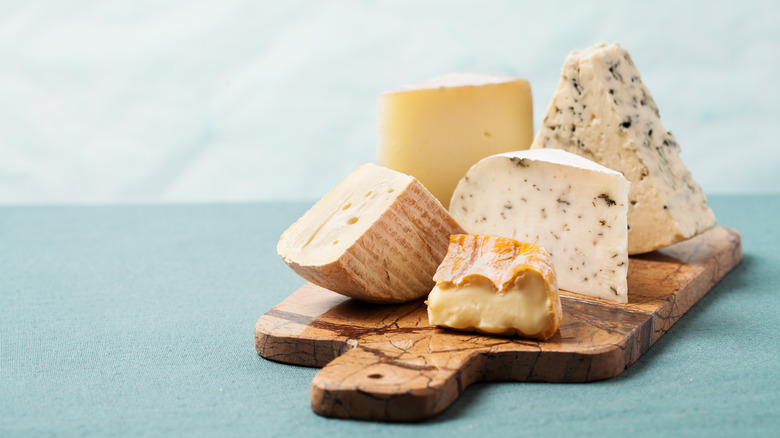
A compound found in aged cheeses can interact with certain antidepressants
Aged cheeses can be a delicacy, especially for all the foodies out there. Cheeses that undergo a longer aging process include cheddar, blue, swiss, parmesan, feta, and more. In the aging process, these cheeses become high in something called tyramine, an amino acid involved in blood pressure regulation. According to WebMD, tyramine is a natural compound found in plants and animals.
And pharmacist Aaron Emmel told Everyday Health that certain antidepressants (monoamine oxidase inhibitors) don't interact well with tyramine. Emmel said, "This combination can cause a hypertensive crisis." And while tyramine is most commonly found in aged cheeses, Emmel added that it's also in "specific types of wine, pickled herring, brewer's yeast, and fava beans."
On top of the interaction with other medications, WebMD also reported that tyramine is a known migraine trigger. If you frequently get migraines or take any MAOIs, it's important to check with your healthcare provider to make sure your diet is low in tyramine.
Taking your medication on an empty stomach could have a variety of negative side effects
When in a hurry, it can be easy to forget to eat a full meal when taking your medications. But some drugs actually require a certain amount of food to reach their full effectiveness.
Pharmacist Mitchell Howard told Everyday Health that medications like Geodon (ziprasidone), which is used to treat bipolar disorder and schizophrenia, require a meal of 500 calories or more for proper absorption. This was confirmed by a 2008 study that revealed that ziprasidone should be taken with food and that the meal should be at least 500 calories "for optimal and reproducible bioavailability of the administered dose."
New York Health Works also noted that aside from impacting effectiveness, taking a variety of medications without a full meal could upset your stomach. If you feel nauseous after taking a medication, try eating a small snack, like a granola bar, the site suggested.
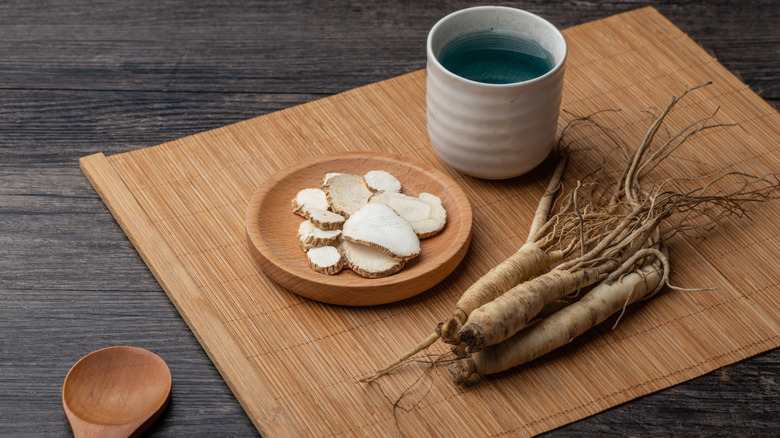
While ginseng has many benefits, it can still interfere with your meds
Ginseng is an herbal supplement that has been used for many centuries in Chinese medicine. It can often be found in teas and it is known for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. And while people have been reaping the benefits of ginseng for centuries, it's also important to know that it can also interfere with certain medications.
According to the American Heart Association, ginseng can "interfere with the bleeding effects of Coumadin. In addition, ginseng can enhance the bleeding effects of heparin, aspirin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen, naproxen and ketoprofen."
Additionally, ginseng is a stimulant, similar in some ways to caffeine, and can impact certain antidepressants. Per the American Heart Association, combining ginseng with these drugs can cause "headaches, trouble sleeping, nervousness and hyperactivity." Consult your doctor or pharmacist before mixing your prescriptions or over-the-counter medications with ginseng.