What Is Tinea Manuum And Who Is Most At Risk?
Dealing with a rash of any form can be both mildly irritating and borderline debilitating as it serves as an unpleasant distraction in your everyday life. It's not easy to concentrate at work or in a classroom when a rash is calling out your name every few seconds, insisting that you scratch it. As reported by the Cleveland Clinic, an individual with tinea manuum will experience a rash as part of their symptoms. There's no doubt the condition has an interesting name, but what is tinea manuum exactly?
Rashes can have many underlying causes, and fungal infections are one of them. Fungal infections are quite common, with up to 25% of people around the world being affected by one. Tinea manuum is a fungal infection that can appear on the palms of the hands, the back of the hands, and between the fingertips. If you're at all familiar with ringworm, you're well on your way to understanding tinea manuum. "Tinea" is the formal name for ringworm, while "manuum" indicates that the infection is located on the hands.
Hand rashes from tinea manuum typically appear as round patches on the skin with raised borders. According to Healthline, the fungal infection can start small and grow over time, spread to other areas of the hand, and cause peeling or flaking of the skin.
Let's take a closer look at who has an increased chance of becoming infected with tinea manuum, and ways to avoid being ambushed by tinea in the first place.
Who is most likely to get tinea manuum?
There are certain risk factors that can make a person more vulnerable to contracting tinea manuum. People who spend time around certain animals have a higher chance of developing tinea manuum being that the infection is contagious. It can spread to humans through animals — including cats, dogs, and cows — as explained by Healthline. The transmission of tinea may be especially prevalent among pet owners who care for exotic animals, such as guinea pigs and hedgehogs, according to a 2022 article published in StatPearls. Engaging in close-contact sports and using public showers may also increase someone's risk of picking up a tinea infection from another person.
Interestingly enough, you can even contract tinea manuum from yourself. Other than the hands, a tinea infection can be found almost anywhere on the body, including the feet, groin, scalp, and beard. As a result, someone who has a tinea infection on another part of their body is at increased risk of transferring the tinea to their hands. For example, someone with tinea on their feet can spread it to their hands if they touch their feet or pick at their infected toenails.
It appears that tinea infections are more likely to occur in men and individuals who live with underlying conditions like diabetes, hypertension, or a suppressed immune system. Tinea manuum can also be more common among people who work in professions that involve constant strain on their hands, such as car mechanics and machine operators.
How is tinea manuum diagnosed and treated?
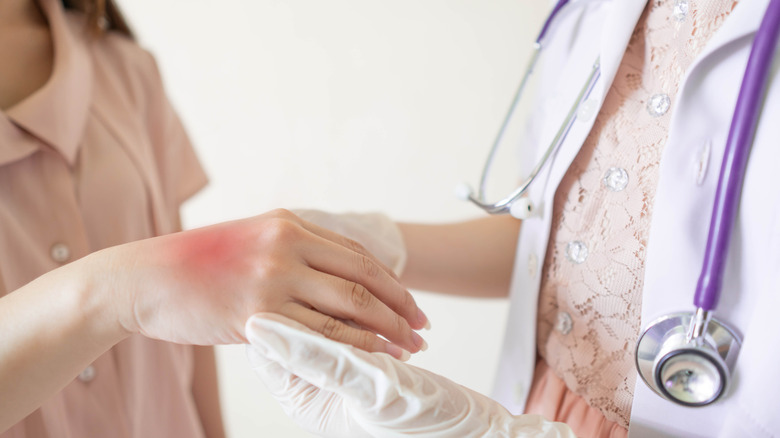
A physician can help determine whether tinea manuum is to blame for the rashes on your hands. Your initial visit will include an examination of the infected area and a discussion of any symptoms you may have, as described by the Cleveland Clinic.
Fungal infections can sometimes be difficult to diagnose, so looking at a rash may not be enough to determine which fungus is responsible. In order to identify the fungus, a skin sample may be collected and observed underneath a microscope with a potassium hydroxide stain. According to Healthline, a Wood's lamp can also be used to diagnose tinea manuum. The lamp is able to detect which fungus is present by emitting a change in brightness compared to the surrounding skin.
Tinea manuum can often be treated at home with over-the-counter topical medications. You may also be prescribed oral antifungal medications if your immune system is weakened, you have recurrent infections, or over-the-counter medications aren't working for you.
There are precautions one can take to reduce their risk of developing tinea manuum in the future. Maintaining proper hygiene by washing your hands frequently and keeping your fingernails clean can help to prevent tinea infections. You should also wash your hands after handling pets and animals, and any pet suspected of having a fungal infection should be examined by a veterinarian. Athletes can avoid infection by showering right after practices, wearing clean uniforms, and not sharing their equipment with their teammates.