The Unexpected Piece Of Technology That Can Reduce Dementia Risk
More than 10 million people around the world will develop dementia this year. It's one of the major causes of disability and dependency, according to the World Health Organization. Dementia is an umbrella term for several types of diseases that progressively damage nerve cells and the brain, with Alzheimer's being one of the most common. Although many older adults will misplace or forget things as a part of normal aging, people with early signs of dementia might find it difficult to solve problems or navigate while walking and driving.
Some risk factors for dementia you can't control, like getting older. People with depression, less education, and living in polluted areas can also be risk factors for dementia. Other factors for dementia you can control, such as being physically active, drinking less alcohol, and managing your weight and blood pressure. Even if you have some of these risk factors already, a 2023 study in The Lancet says it's possible to cut your dementia risk in half. The secret? Get a hearing aid right away when you notice signs of hearing loss.
The link between hearing and cognitive decline
The study involved people aged 70 to 84 who were already noticing signs of hearing loss, but didn't show signs of cognitive impairment. One group was fitted for hearing aids while another group received health-related education. Although the researchers didn't find differences in cognition between groups after three years, further analysis showed that hearing aids had an effect on one population. A group that had already risk factors for cognitive decline scored worse on cognitive tests if they didn't have the hearing aid.
Researchers told the Washington Post that there are three theories why people with hearing loss might suffer from cognitive decline. First, it takes a lot of brain power to understand others when you're struggling to hear. This leaves less energy to process the information. Second, the part of the brain responsible for hearing begins to shrink when it's not receiving information. This could subsequently affect other parts of the brain. The third theory hypothesizes that people may withdraw from socializing. The rationale is that someone may not feel comfortable talking with others when it's difficult to hear them. Consequently, the mind becomes less stimulated by the lack of socialization.
What to do about hearing loss
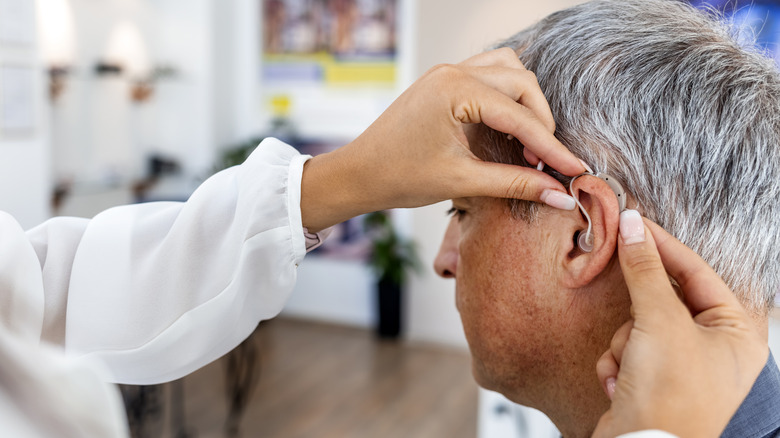
Knowing the signs of hearing loss can help you decide if you need to see a doctor. Some signs include people telling you that you shout when you speak to them or needing a television to be louder than other people's levels. Straining to hear, needing people to repeat themselves, and believing people are mumbling are also signs of possible hearing loss. A hearing aid can help you communicate better with others, and you might find that you can hear sounds and speech much better than before.
It's important to know, however, that hearing aids can't give you perfect hearing. They can also amplify background noises you might find distracting. For example, you could hear radio frequency emissions from your cell phone, which can make it difficult to hear a phone conversation. Some phones will have a label indicating their compatibility with hearing aids.
Anyone over 18 can now buy an over-the-counter hearing aid without having to see a doctor. Prescription hearing aids don't require a medical examination, but some states still require you to see a hearing specialist first.