This Is What Happens To Your Heart When You Don't Drink Enough Water
Water is essential to your body. According to the Mayo Clinic, water makes up around 60% of body weight. It plays a vital role in keeping you healthy by regulating your body temperature, lubricating your joints, protecting your organs and tissues, and even carrying the necessary nutrients and oxygen to your cells. The amount of water you need daily varies depending on factors such as age, sex, weight, and activity level. Men are recommended to drink at least 12 cups of fluid daily, while women require a minimum of 9 cups. However, almost half of adults in the U.S. don't drink enough water to meet the recommended daily intake, according to a 2023 CivicScience poll.
Dehydration occurs when you lose more fluids than you consume, which can seriously affect your body. It can even take a toll on your heart. The Heart Foundation explains that when your body is dehydrated, your blood volume decreases. This can lead to other, more serious issues.
Cardiovascular consequences of dehydration
A 2019 study published in Nutrients showed the close connection between hydration and cardiovascular health. When your body doesn't have enough water, your blood becomes thicker, so less of it circulates through your veins and arteries. Your heart must work harder to compensate for the reduced blood volume. Your heart beats faster, so it can deliver blood to all your vital organs and tissues.
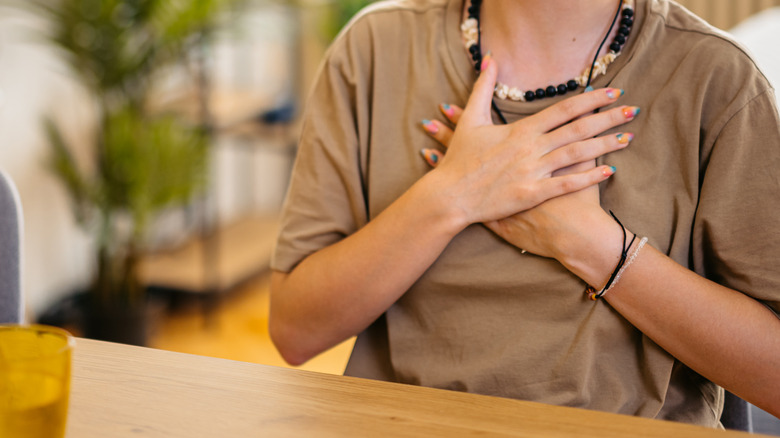
This can increase your heart rate and blood pressure (per Healthline), leading to palpitations. Palpitations are the sensations of a rapid, fluttering, or pounding heartbeat that may feel like your heart is beating irregularly, forcefully, or too fast. The Cleveland Clinic reports that dehydration can also raise blood pressure by causing blood vessels to constrict. In addition, the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center states that dehydration can cause your blood pressure to drop, making you feel dizzy or lightheaded and sometimes leading to fainting.
When to seek medical attention and considerations for heart health
If you are concerned about the effect of dehydration on your heart, it is crucial to know when to seek medical attention. According to Healthline, you should see a healthcare professional soon or get emergency medical attention if your heart palpitations come with other symptoms or if the symptoms are persistent and bothersome. Symptoms that may indicate a serious underlying health condition include dizziness, shortness of breath, chest pain, excessive thirst, sweating, nausea, and feeling lightheaded.
If you have been diagnosed with heart failure, you may need to limit your water intake to avoid fluid buildup in your body (per Medline Plus). Your doctor can provide you with specific guidelines on how much water you should drink daily and how to monitor your fluid intake.
In general, it is essential to drink enough water to avoid dehydration and its effects on the heart. Drinking fluids should be enough to relieve mild dehydration, but severe dehydration can be life-threatening and requires medical attention.