The State With The Most Deaths From Hypertension In 2021 May Surprise You
Otherwise known as high blood pressure, hypertension is a chronic condition that often precipitates more severe health issues down the road, according to the Mayo Clinic. In cases of hypertension, your heart increases the amount of force required to pump blood through narrowed arteries. Subsequently, having prolonged high blood pressure increases one's risk for cardiovascular disease and stroke.
Most people are not aware that they have high blood pressure, reports the Mayo Clinic. The typical reason for this is that the condition can exist with no clear symptoms for years. In order to determine whether or not your blood pressure is within normal range, it's important to have it checked at least every two years by your physician.
Millions of people in the U.S. are currently diagnosed with hypertension, according to Million Hearts. Of the estimated 116 million Americans with the condition, the vast majority, 92.1 million, do not have it adequately under control.
Factors that contribute to rates of hypertension
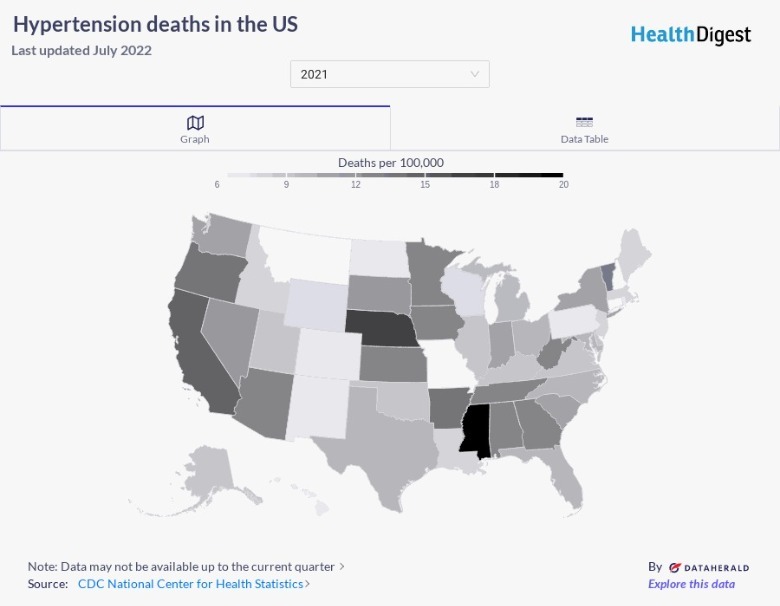
Untreated cases of hypertension can become life-threatening, and data reveals that mortality rates can vary greatly by state. In 2021, the state with the greatest number of deaths related to hypertension was Mississippi, with 20.4 per 100,000 people. The state with the second highest number of deaths was Nebraska, with 16.7 per 100,000 individuals. California ranked third highest, with 14.8 per 100,000 dying from hypertension. The state with the lowest numbers of hypertension-related deaths in 2021 was New Hampshire, with 6.4 mortalities per 100,000 people. Missouri came in close behind at 6.5 deaths per 100,000.
Research from a 2020 analysis published in the International Journal of Cardiology Hypertension took a look at what potential factors contribute to prevalence rates of hypertension across the U.S. Findings revealed that older adults, males, and obese individuals, as well as those with diabetes or chronic kidney disease, proved to have higher rates of hypertension. Lack of health insurance also proved to be a contributing factor, thereby highlighting existing health disparities across the country.
To help reduce one's chances of developing high blood pressure, the CDC encourages individuals to eat a healthy diet, engage in regular physical activity, refrain from smoking, limit alcohol consumption, and maintain adequate sleep.