Unexpected Health Benefits Of Quinoa
Quinoa has become increasingly popular over the years due to its nutritional value and versatility in cooking. As a 2021 study published in Plants explains, it is a pseudo-cereal, which means that it is similar in its nutritional profile and can be used like cereal grains such as wheat or rice, but actually belongs to the same botanical family as spinach and beets. Quinoa has been cultivated for over 3,000 years and is native to the Andes region of South America. However, it finally made its way to the rest of the world in recent years, where its nutritional qualities, health benefits, extensive culinary uses, and role in eradicating hunger and malnutrition led the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) to declare 2013 as the "International Year of Quinoa."
Quinoa seeds — the part of the quinoa plant destined for human consumption — are tiny and light. In fact, it takes about 350 quinoa seeds to reach one gram of the food. To prepare quinoa, first, rinse it thoroughly in a fine-mesh sieve to remove any impurities, and then cook it like you would cook rice by combining one part quinoa with two parts water or broth, boiling it, and finally simmering it until the liquid is absorbed and the quinoa is tender. Cooked quinoa can be used as a base for salads, served as a side dish, added to soups, or used in place of rice in many recipes. Aside from being delicious and nutritious, quinoa has many health benefits to offer. Keep reading to discover some unexpected health benefits of quinoa.
Quinoa is loaded with vitamins and minerals
Quinoa is a nutrient-dense food rich in several essential vitamins and minerals. In fact, due to its high nutritional value, some would argue that it can be considered a "superfood," a term used to describe foods that are rich in nutrients that are important for optimal health, such as antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals (via the Cleveland Clinic).
For example, according to a 2021 study published in Plants, quinoa is a good source of magnesium, iron, and phosphorus, providing 26%, 14%, and 21% respectively of their recommended daily intakes per one cup of cooked seeds. Magnesium is a mineral important for many bodily functions, including energy production and nerve and muscle function. As for iron, it is essential for the formation of red blood cells and the transport of oxygen throughout the body. Lastly, phosphorus is key for bone health and the production of DNA and cell membranes.
Additionally, quinoa contains a variety of B vitamins, including folate, thiamin, and riboflavin, which play important roles in DNA formation, energy metabolism, and the maintenance of healthy skin, hair, and nails. Moreover, the study states that quinoa also contains vitamins C and E, which have antioxidant properties that may help protect against harmful free radicals and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
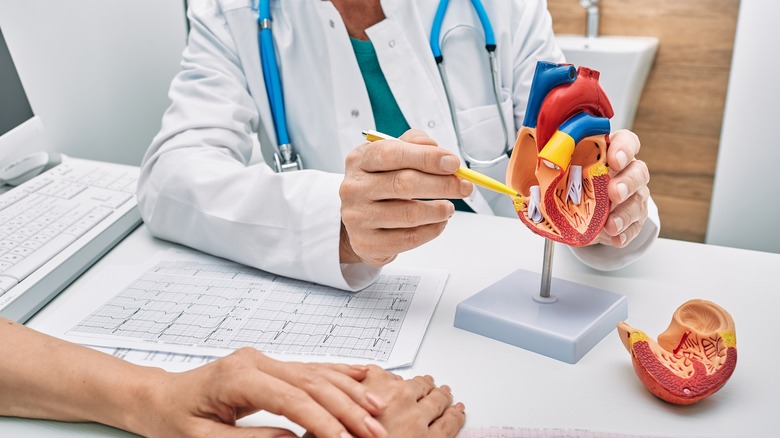
It may improve your heart health
One of the several potential health benefits that quinoa holds includes a reduced risk of heart disease, due to its beneficial effects on lowering blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels and blood pressure, which, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), are two risk factors that can lead to different heart conditions such as heart attacks, heart failure, or arrhythmias. For example, according to a study published in the International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition, consuming 25 grams of quinoa flakes led to a significant reduction in total cholesterol, LDL ("bad") cholesterol, and triglyceride levels compared to the same amount of corn flakes. Similarly, another 12-week study published in Current Developments in Nutrition found that a daily intake of 50 grams of quinoa significantly reduced triglyceride levels in people with obesity. Researchers attributed the results to quinoa's high fiber content, which is known to improve blood cholesterol levels.
In addition to these effects, quinoa may also help lower your blood pressure. According to an animal study published in Nutrients, the digestion of quinoa proteins may lead to the production of active metabolites or byproducts that help regulate blood pressure between 2 and 10 hours of ingestion.
Quinoa may help control your blood sugar levels
Like many other whole grains, quinoa can help you keep your blood sugar levels in check, which is especially beneficial for people with diabetes. As the CDC explains, diabetes is a long-term condition that affects the way your body processes sugar, leading to high blood sugar levels, which is detrimental to your health as it increases the risk of other conditions such as heart and kidney disease.
Nevertheless, quinoa has a couple of tricks up its sleeve to help you manage your blood sugar. On the one hand, Healthline explains that quinoa has a glycemic index (GI) of 53. The GI is a measure of how foods affect your blood sugar levels, and scores under 55 are considered low, meaning these foods are absorbed more slowly and cause a steady increase rather than a spike in your blood sugar. On the other hand, quinoa's high fiber content also plays a role in regulating blood sugar levels. As a study published in Nutrients explains, fiber can slow down the digestion and absorption of glucose into the bloodstream, which leads to lower blood sugar levels after a meal. Thus, unlike refined grains and sugary foods, which can cause rapid fluctuations in blood sugar levels, quinoa provides a steady release of energy over time.
It may help you manage your weight
Adding quinoa to a healthy and balanced diet can be a great way to support a healthy weight, and maintaining a healthy weight is important for overall health, seeing that being overweight or obese can increase the risk of several chronic diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancers, the CDC explains. One of the ways that quinoa may help with weight management is through its high fiber content. As a study published in Nutrients explains, research has found an inverse association between the amount of fiber you eat and your body weight, meaning that higher fiber intakes usually lead to lower body weights (and vice versa) due to fiber's effect on satiety or fullness.
Additionally, aside from its fiber content, quinoa contains a unique protein composition, which is an influential nutrient for weight management. Per a review published in Regulatory Peptides, protein increases energy expenditure and promotes the production of hunger-reducing hormones, which helps regulate your appetite. Thus, both quinoa's fiber and protein content lead to increased feelings of fullness, which can help reduce your overall calorie intake and promote a healthy weight.
It is naturally gluten-free
According to Healthline, quinoa is a naturally gluten-free food that is a great option for people with celiac disease, gluten sensitivity, or other conditions that require a gluten-free diet. Per a 2022 review published in the Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, gluten is a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, as well as some processed foods, and for people with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, consuming gluten can cause an immune reaction that damages the small intestine and can lead to a range of symptoms and consequences such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, and nutrient deficiencies.
Per the Mayo Clinic, there's no cure for celiac disease, and the only way to treat it is by avoiding gluten-containing foods altogether, which can be highly restrictive. Luckily, quinoa is a great alternative for people with celiac disease, and since it is highly nutritious, it is an excellent option for people following a gluten-free diet who may be at risk for nutrient deficiencies due to the diet's restrictive nature.
Quinoa may promote gut health
Maintaining a healthy gut is essential for overall health and wellness. As a review published in Frontiers in Microbiology explains, the gut microbiome (your gut's friendly bacteria) plays a key role in several bodily processes, including digestion and immune function. An imbalance in the microbiome (also known as dysbiosis) may affect not only your gut but also your metabolic health and even your mental health. However, the review states that one easy way to care for your gut health is by eating enough fiber because, while humans cannot digest it, it is the primary food source for the bacteria in your gut, and its intake can determine whether you have a healthy gut or not.
One of the ways that quinoa may benefit gut health is through its high fiber content, namely its soluble fiber content. According to a study published in Nutrients, quinoa's soluble fiber acts as a prebiotic or food for your microbiota, which produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) after digesting it. These SCFAs boost your gut and immune health by improving the lining of your gut and reducing inflammation in your body. Another way quinoa may promote gut health is through its antioxidant content. Per the study, antioxidants support a healthy and diverse gut microbiome, reduce inflammation, and fight disease-causing bacteria thanks to their antibacterial properties.
It is a plant-based, high-quality protein source
Quinoa is often considered a superfood due to its nutrient density, and one of its standout features is its impressive protein content. For starters, a 1-cup serving of cooked quinoa packs 7 grams of protein, which is a lot compared to what other gluten-free cereal grains provide. For example, the same serving of cooked white rice provides just 3 1/2 grams of the nutrient, or half of quinoa's protein count.
In addition, unlike other grains, quinoa is considered a complete protein because it packs all nine essential amino acids — these are the ones you need but your body can't produce (via Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health). This is rare in plant-based foods and is what sets animal-based and plant-based proteins apart, because most plant-based proteins are incomplete, meaning that they lack one or more essential amino acids. In fact, quinoa is considered such a good protein source that a study published in Plants compares its quality to that of cow's milk. Thus, this makes quinoa an ideal choice for vegetarians, vegans, and anyone looking to incorporate more plant-based protein into their diet.
It is a rich source of antioxidants
Antioxidants are beneficial compounds that can help protect your body against damage from free radicals (via Healthline). Free radicals are unstable molecules that, despite being produced naturally in the body as a result of normal metabolic processes, can actually damage your cells and lead to harmful health effects when produced in excessive amounts. Factors such as pollution, smoking, and exposure to UV radiation can increase the production of free radicals, leading to oxidative stress and inflammation, which scientists have linked to DNA damage (which is associated with premature aging and a risk factor for cancer).
Nevertheless, being a nutritional powerhouse, quinoa is packed with antioxidants. According to a review published in Molecules, quinoa has over 190 beneficial plant compounds, including antioxidants such as phenolic acids and flavonoids. Both the review as well as a study published in Plants state that said antioxidants in quinoa offer numerous health-promoting effects, including blood pressure-lowering properties and antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer effects, meaning that they have protective effects against chronic diseases. In addition, per the review, quinoa's antioxidants may also benefit the body in other ways. For example, they may help to improve immune function, promote healthy skin, and even improve mental function.
It is highly nutritious but also contains anti-nutrients
While quinoa is generally considered to be a highly nutritious food, it does contain a few anti-nutrients. Anti-nutrients are compounds in foods that can potentially interfere with nutrient absorption and digestion (via Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health). Thus, they can potentially lead to nutrient deficiencies if quinoa is consumed in large amounts or on a regular basis without first removing these anti-nutrients.
According to a review published in Molecules, one type of anti-nutrient found in quinoa is saponins, which are bitter-tasting compounds found in the outer layer of the quinoa seed. While saponins may have some health benefits, such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-cancer properties, they can also interfere with nutrient absorption by binding to minerals such as iron, zinc, and calcium. Like saponins, phytate is another anti-nutrient present in quinoa that can lead to the malabsorption of minerals like iron and calcium, a study published in the journal Discover Foods explains. However, both sources agree that anti-nutrients in quinoa can be easily removed by soaking or rinsing the seeds thoroughly in water before cooking. This ultimately makes other important nutrients in quinoa available for absorption, meaning that you can reap the many nutritional benefits while minimizing the potential impact of any anti-nutrients present.